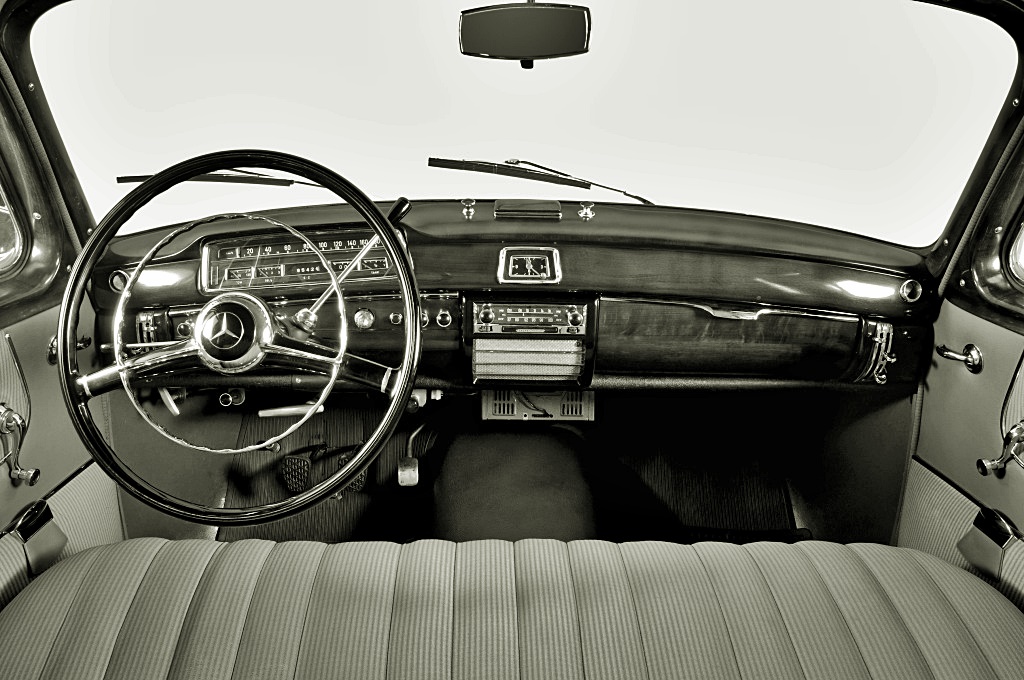
The vehicle dashboard – that area below the windscreen at the front of the cabin – began with one side being dedicated to the driver (and associated with the ‘cockpit’ of an aircraft) and the other for the front passenger. It was generally like that for decades, the surface of the dashboard punctuated by various controls, switches and other ornamental decorations.
As more electronic systems were installed and more information could be presented on displays, the cockpit area widened. Then came infotainment, when more than just a radio or CD-player provided entertainment; as connectivity grew, the dashboard came the be used to house various systems which even passengers used and even wider displays appeared.
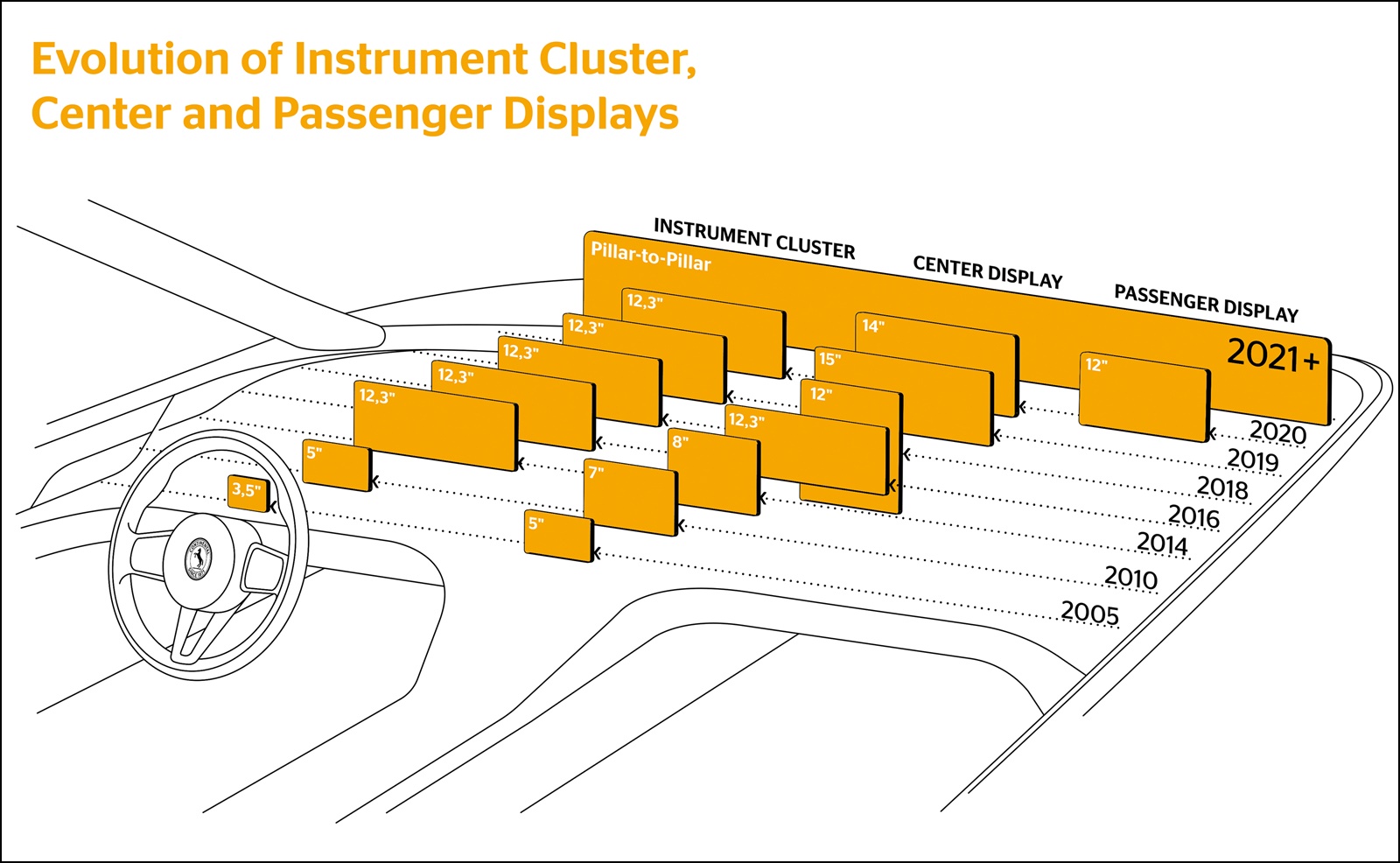
From pillar to pillar
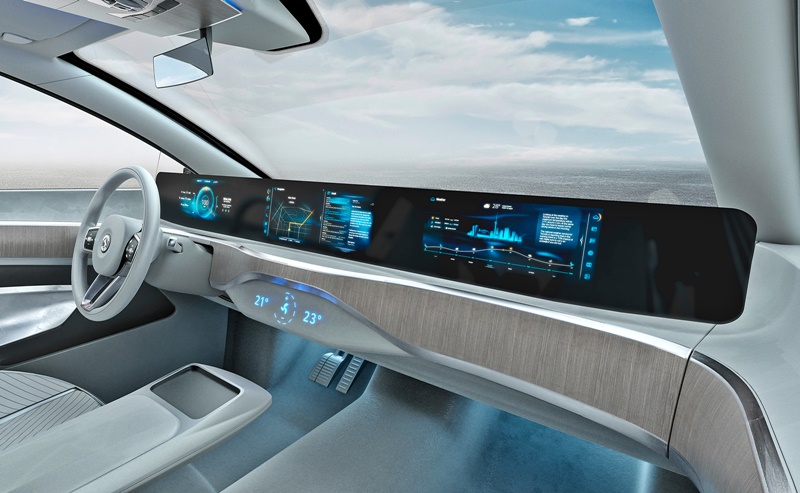
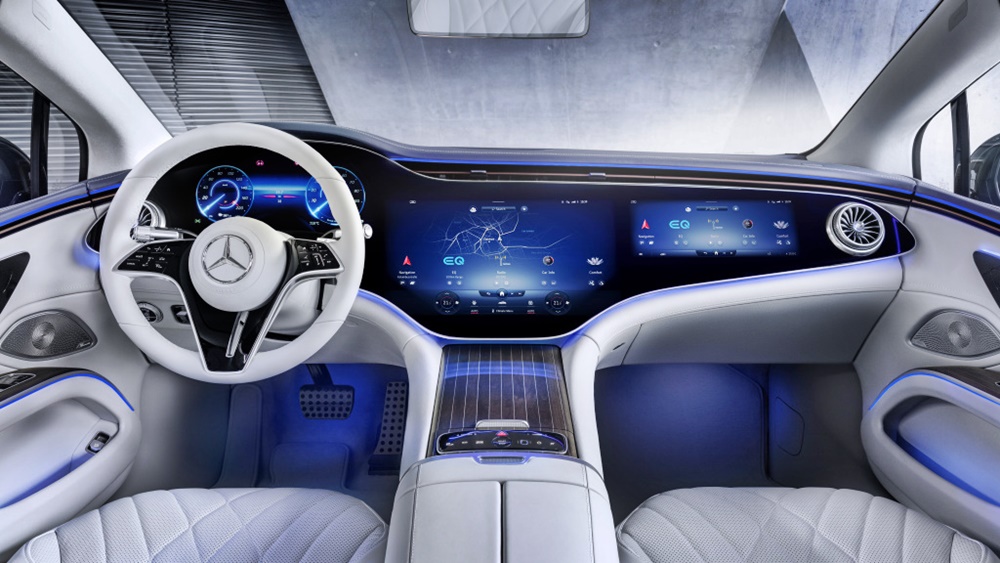
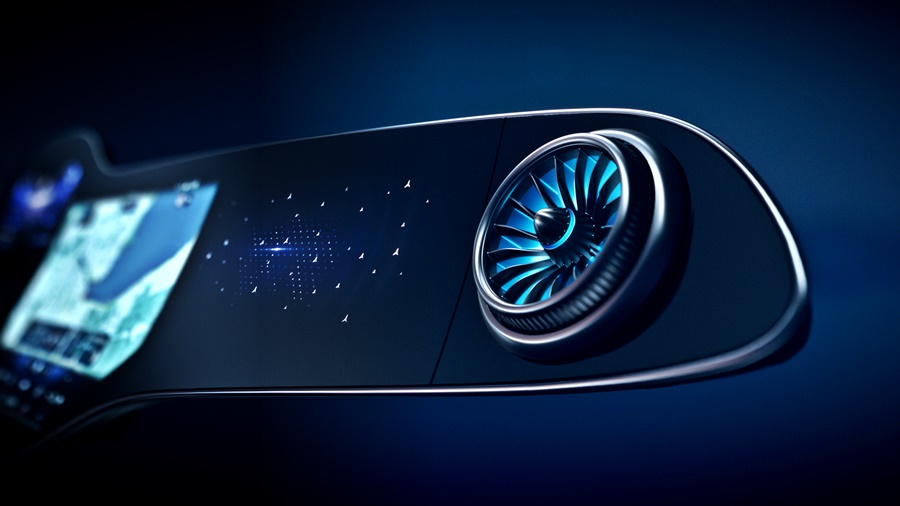
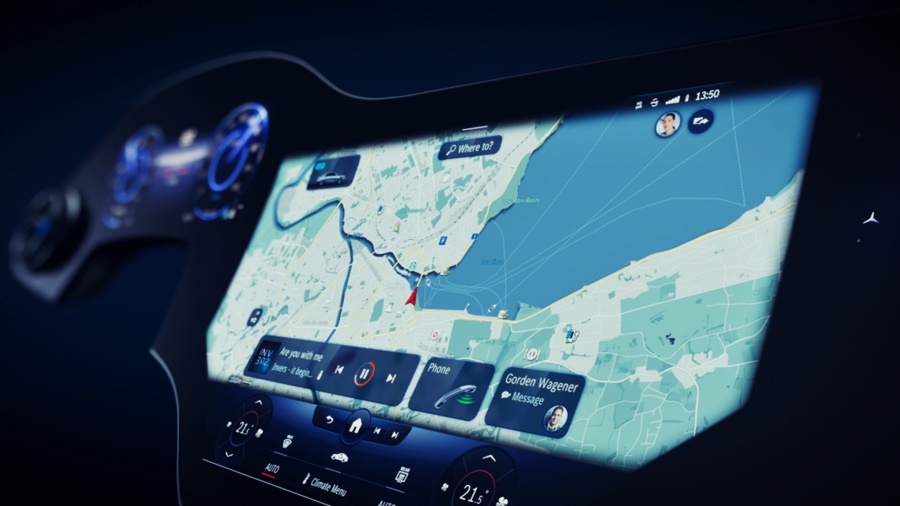
Now, as we have seen with some of the latest Mercedes-Benz models, huge displays extend the full width of the dashboard to provide all kinds of information for the driver and other occupants. Fifty years ago, such an idea may have been seen only in concept cars but are now becoming a reality in production models the public can buy.

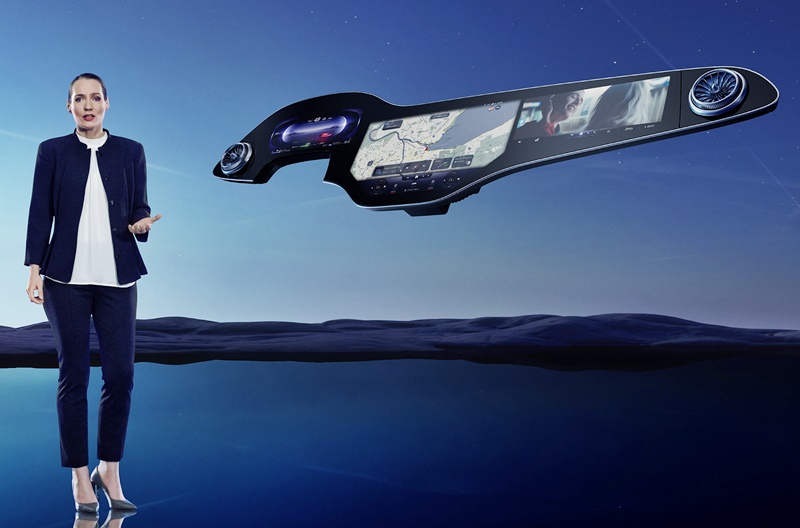
The concept won’t be limited to a few brands as Continental has developed a pillar-to-pillar display and it is available to any carmaker. In fact, one global vehicle manufacturer has already placed a major order with Continental and will have the super-wide display in a production model in 2024.
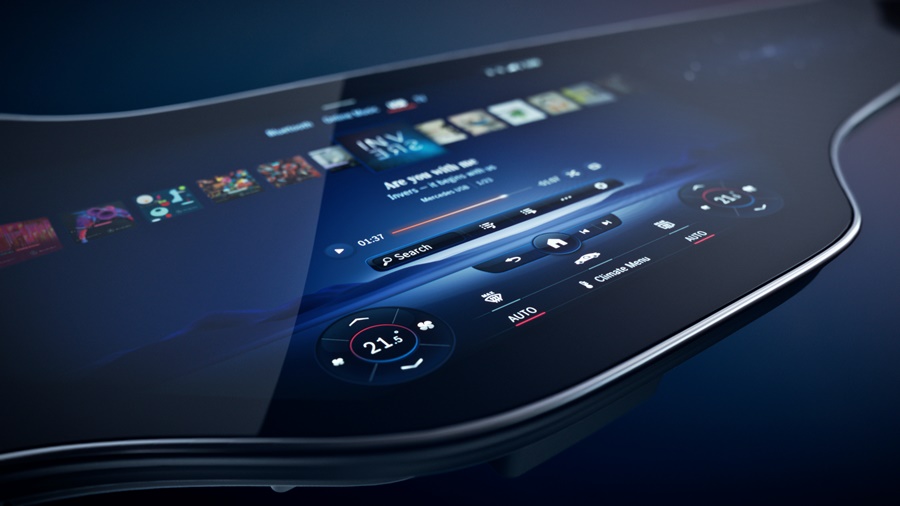
Continental’s display that extends across the entire width of the dashboard is an integrated display solution from one roof pillar to the other at the front, providing space for a growing number of vehicle functions, digital services, as well as communication and infotainment applications. The solution makes the display the central visual interface between the driver, front passenger and digital driving experience.
Milestone in evolution of the car
Its launch in a high-volume production model marks another milestone in the evolution of the car into a smart device as part of the internet of things (IoT). Whether it is navigation, warning signs, movies, news, social networks, office applications or booking apps to plan the route, the information will be shown and easily viewed. Continental adds that the content will be ‘fully immersive and offers drivers and passengers a completely new user experience’.
“A driving experience that is digital and safe is becoming the most distinctive feature of modern cars. The size of the displays and their intuitive operation play a central role here. In short, what used to be horsepower is now screen diagonals and user experience,” said Dr. Frank Rabe, Head of the Human Machine Interface business unit at Continental.
“With the user experience, we already create value today. Each year, we supply a total of around 120 million products for human-machine interaction, equipping one in four cars worldwide. With the increasing significance of automated driving, the way in which we spend our time in cars is becoming even more important. As a result, there is also a growing need for solutions and services for the in-vehicle user experience.”
From pointer instruments to digital displays
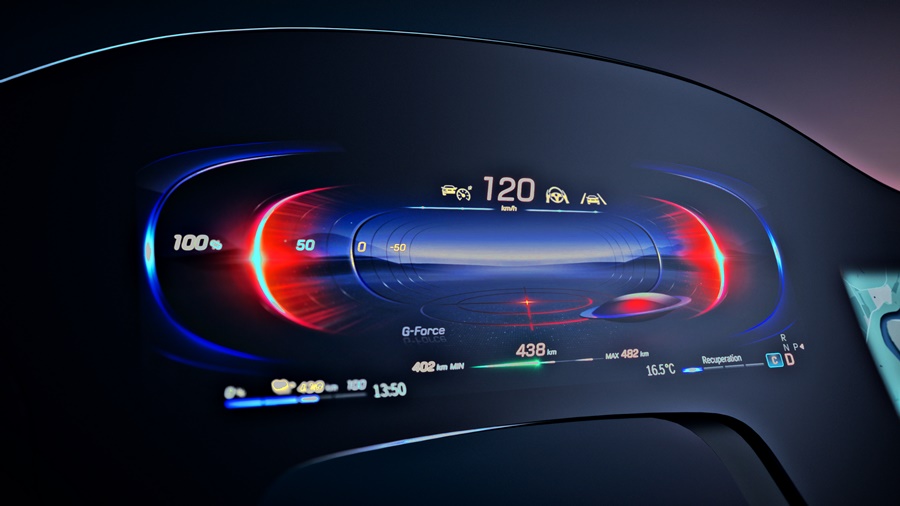
Speedometer, tachometer, fuel consumption gauge – the time of the classic instrument panel is over. In view of the multitude of new vehicle functions and digital services that are pushing into cars with increasing connectivity, traditional pointer instruments and centre consoles are now too rigid and inflexible. The switch to vehicles with electric powertrains also changes some of the running information that has to be shown.
An exclusive focus on the driver is also no longer appropriate for the wide range of communication and infotainment services now available for vehicle occupants. Therefore, displays have been getting bigger and bigger for years. This also poses design challenges which, over time, have resulted in different shapes: from flat displays to curved displays that fit seamlessly into the cockpit, into V, C, L or S-shaped displays, accommodating both the driver and the front passenger, so that they can be reached with minimum effort.
As the size increases, several displays are connected under one surface to form a single unit. Creating invisible transitions is not the only crucial aspect here. Sensors and cameras that record driver behaviour can be seamlessly integrated. Convex and concave shapes are also increasingly being used so that the user can perceive the operating elements intuitively.
Transforming vehicle electronics architecture
Whether it is 3D without special glasses or pillar-to-pillar displays, Continental has been a pioneer in this digital cockpit evolution. In addition to the further development of screen solutions, the company is also driving forward the transformation of the vehicle electronics architecture with concepts such as the high-performance computer for the cockpit. In view of the fact that a few high-performance computers will replace the previous large number of dedicated control units in the future, the pillar-to-pillar display is the next evolutionary step and an expression of the increasing convergence of the car to a mobile data centre.