For many who have been in a car when it has been involved in a serious accident, the safety features that they may thank for having saved their lives would likely be the seatbelt and perhaps the airbag as well. There’s no doubt that these two safety features have saved tens of thousands of lives and reduced the severity of injuries for many thousand more.
However, just as vital to preventing deaths and reducing injuries has been the structure of the car itself. This is what has first contact with another object – a vehicle, a tree, a lamp post or even a building – and it receives the enormous forces of impacts. These forces are transmitted through the body and each the cabin where they can cause injuries as various parts are smashed into humans.
Thanks to pioneering work by a Daimler Benz engineer in the late 1940s, modern car structures have been engineered in such a way as to diminish the impact forces so they do not cause great harm. The engineer was Béla Barényi and his innovation – called the passenger car safety cell – is a fundamental feature of passive automotive safety to this day. It was patented in Germany by Daimler-Benz and described as ‘a passenger car body with a passenger safety cell’. The Patent No. 845 157, which also identified Barényi as the inventor, had the title ‘Motor vehicle, specifically for personal transport’.
The engineer was fortunate to work at Daimler-Benz which was just as passionate about safety as he was. There were other carmakers at that time who carefully avoided topics about crash safety; particularly in the post-war period, nobody wanted to be reminded about the dangers of driving. The topic was viewed as a sales killer right up to the 1970s.
Barényi’s innovation had completely changed how vehicle construction should be with regard to occupant protection. For decades, engineers had taken the approach that the more rigid the body could be made, the better the protection would be during an accident. So a tank would have been very safe – but rather impractical on public roads.
Barényi’s studies showed that that the forces generated during an impact were transferred to the occupants with hardly any prior absorption. And with no seatbelts to retrain them (airbags would come 30 years later), they would also be thrown about the cabin, if not out of it.
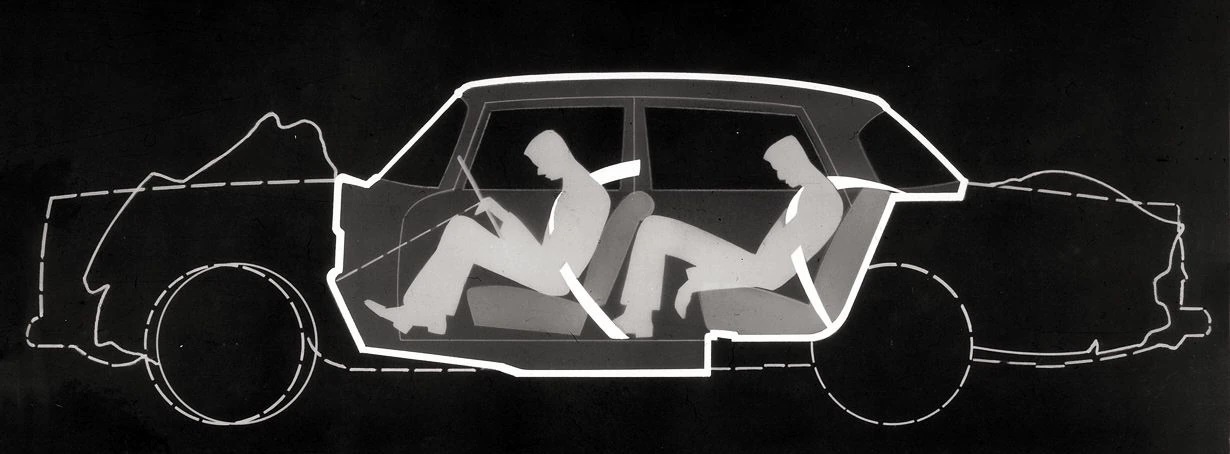
These findings led Barényi to find a way to have absorb the kinetic energy built up during a collision. He came up with an overall vehicle concept which consisted of three cells: the safety cell in the middle where the occupants were seated, and cells at the front and rear which were connected to it. This concept was developed some years earlier when Barényi did his own ‘Terracruiser’ and ‘Concadoro’ studies, and when he joined Daimler-Benz, he was able to realise them.
The text of the patent application explained the purpose of this design as follows: “The forces generated during a collision are […] absorbed by the [front or rear] cell section.” Later on, a catchy expression was coined for these areas of controlled deformation: crumple-zones. The safety cell that encircled the occupants and protected them from the impact forces acting on the vehicle structure also came to be referred to as a ‘safety cage’.
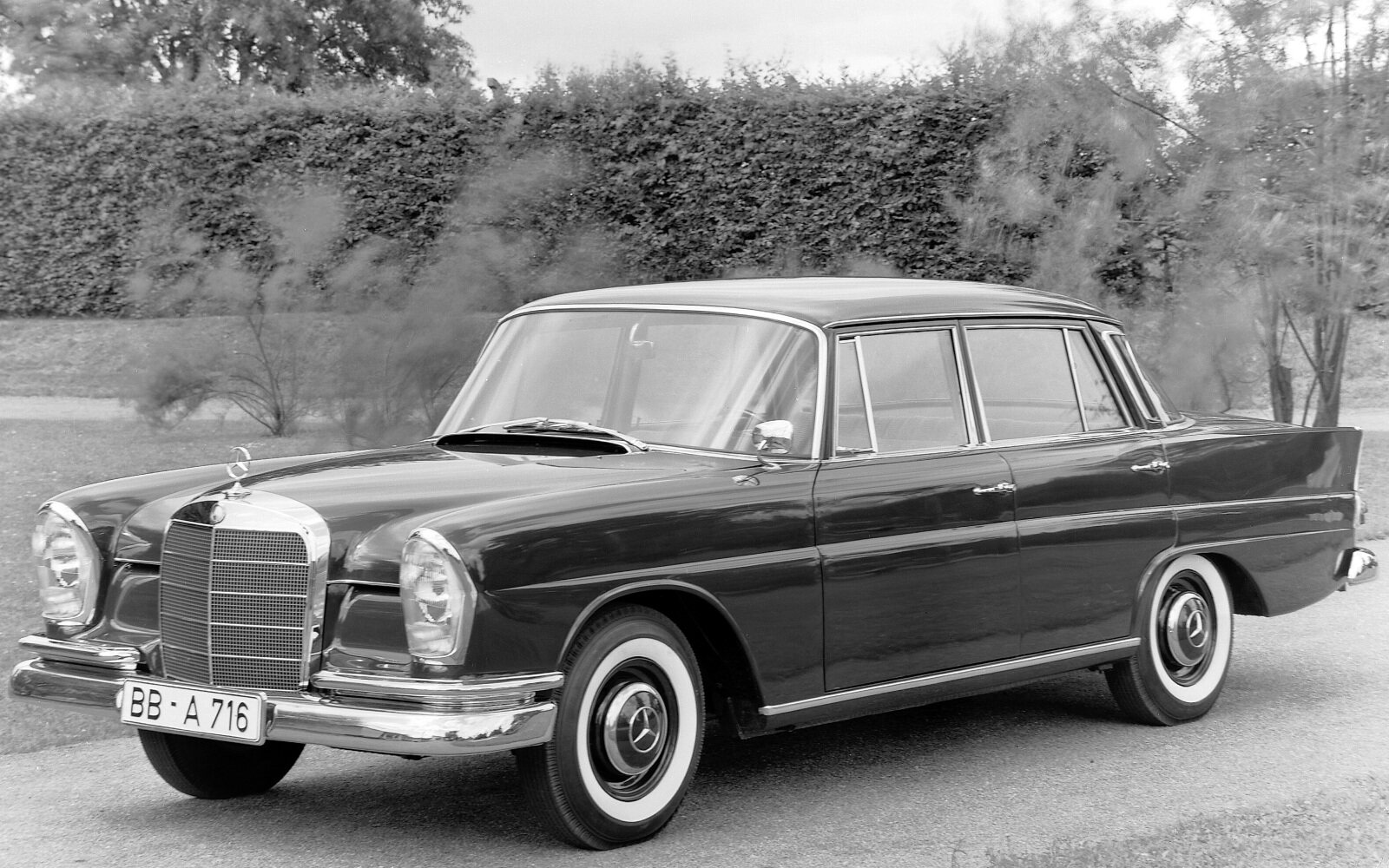

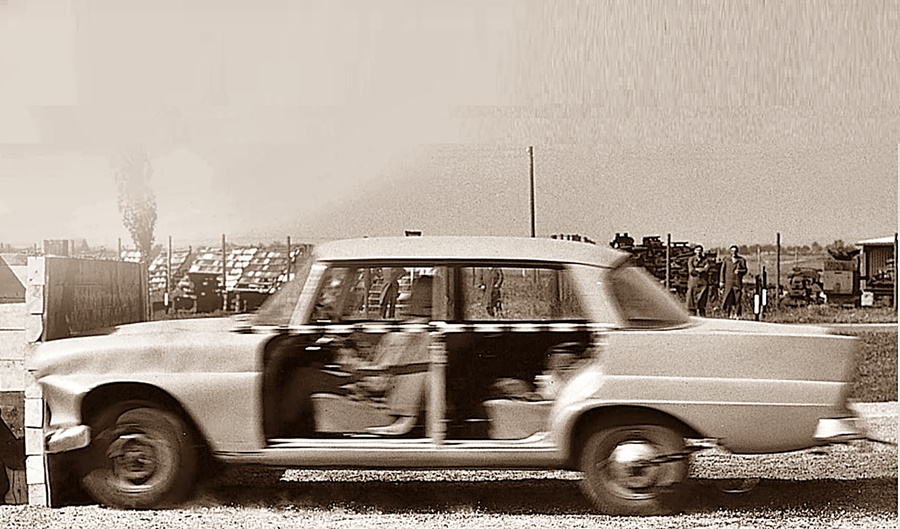
In 1959, the safety body with its rigid passenger cell was used for the first time in a production model – the Mercedes-Benz W 111 series which had the distinctive ‘fintail’. Mercedes-Benz also increased the awareness of developers where automotive safety in general was concerned. The W 111 model also had a new safety steering wheel (also developed by Barényi) with a large impact plate and a deformable connecting piece between the plate and the end of the steering column, which was moved forward.
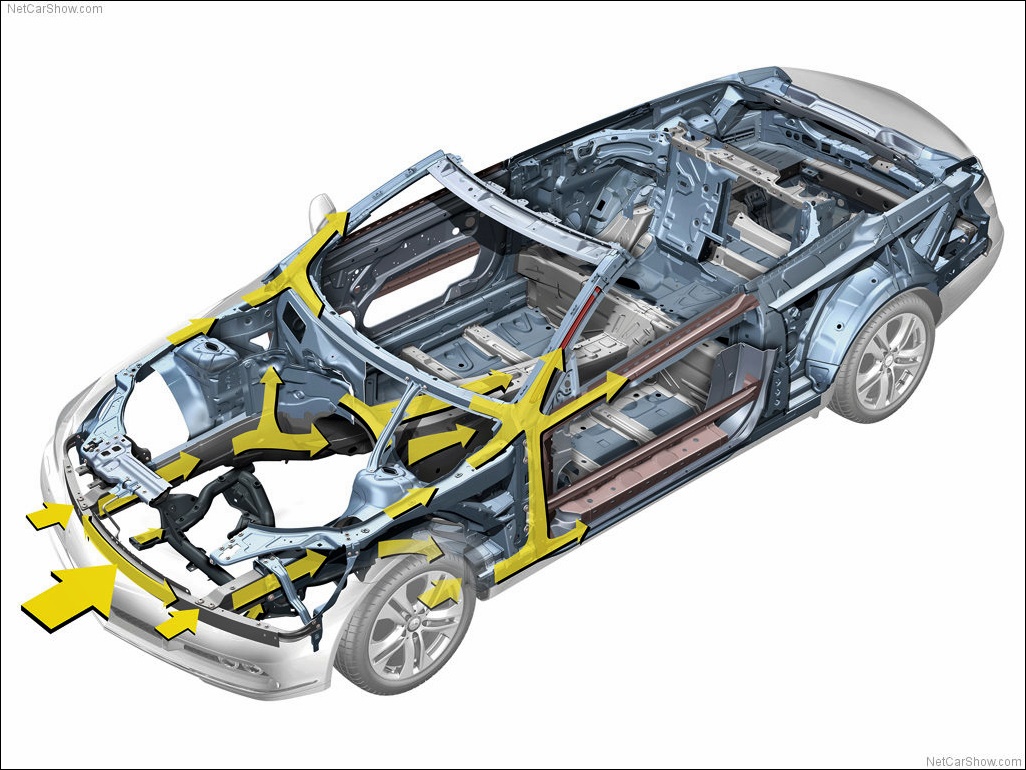
With new technologies, especially computer-aided engineering, the concept of the safety cell has evolved further. The impact forces are not just absorbed but also dissipated by carefully designed structural members to provide ‘paths’ around the cabin area. Nevertheless, the fundamental objective remains and that is to prevent or minimize the forces that reach the occupants. Béla Barényi received more than 2,500 patents for his inventions, most of which related to automotive innovations and enhancements.
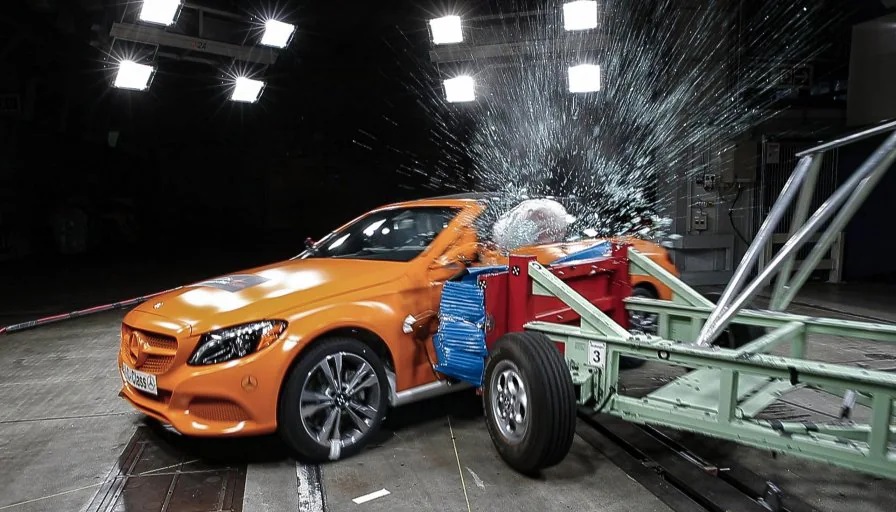

All-new Mercedes-Benz S-Class set to be a pioneer in safety features again (w/VIDEOS)