Since the late 1990s, hybrid powertrain systems have been developed by various manufacturers, acting as the first step in electrification of vehicles. The systems are similar in having an electric motor and a combustion engine but differ in the way they operate. The ideal operating strategy is to be able to use the electric motor as much as possible, with the engine coming in when extra power is needed.
Nissan’s e-POWER system takes a slightly different approach although it has the motor and engine as well. Part of the electrification strategy under Nissan Intelligent Mobility, e-POWER borrows from the EV technology developed for the LEAF, now the best-selling fully electric car in history.
Nissan Intelligent Mobility anchors critical company decisions around how cars are powered, how cars are driven, and how cars integrate into society. In 2006, Nissan R&D was able to achieve a breakthrough in its energy management technology by reducing the battery capacity to match its competitors’ hybrid vehicles while still delivering desirable EV qualities, such as quietness and efficient energy use. In addition, application of Nissan’s technologies, such as the integration of a power-generating engine, electric motor drive for compact car use, strengthening of the powertrain’s rigidity and improvements in NVH levels, became the foundation of e-POWER and its implementation in the compact-car segment.
Where the LEAF requires regular recharging of its battery pack, an e-POWER system does not need that as a small petrol engine is used to charge the high-output battery pack when necessary. This means that the driver will have no need to look for a charging station (or set one up in his home) and no ‘range anxiety’ (the fear of running of out electricity and being unable to recharge).
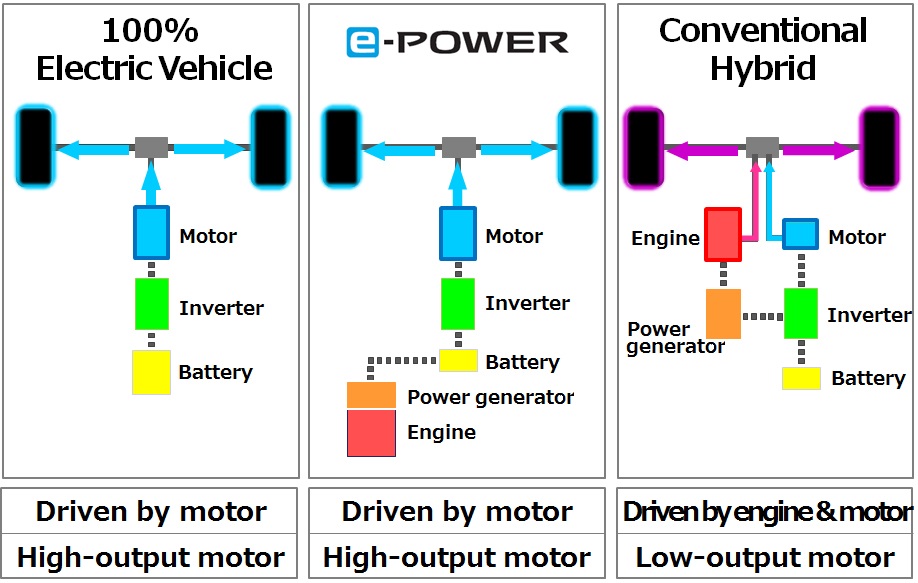
A significant difference between the e-POWER system and other hybrid systems is that the wheels are driven only by the electric motor. With other hybrid systems, the motor and engine are used to propel the vehicle, varying their amount of contribution according to driving conditions.
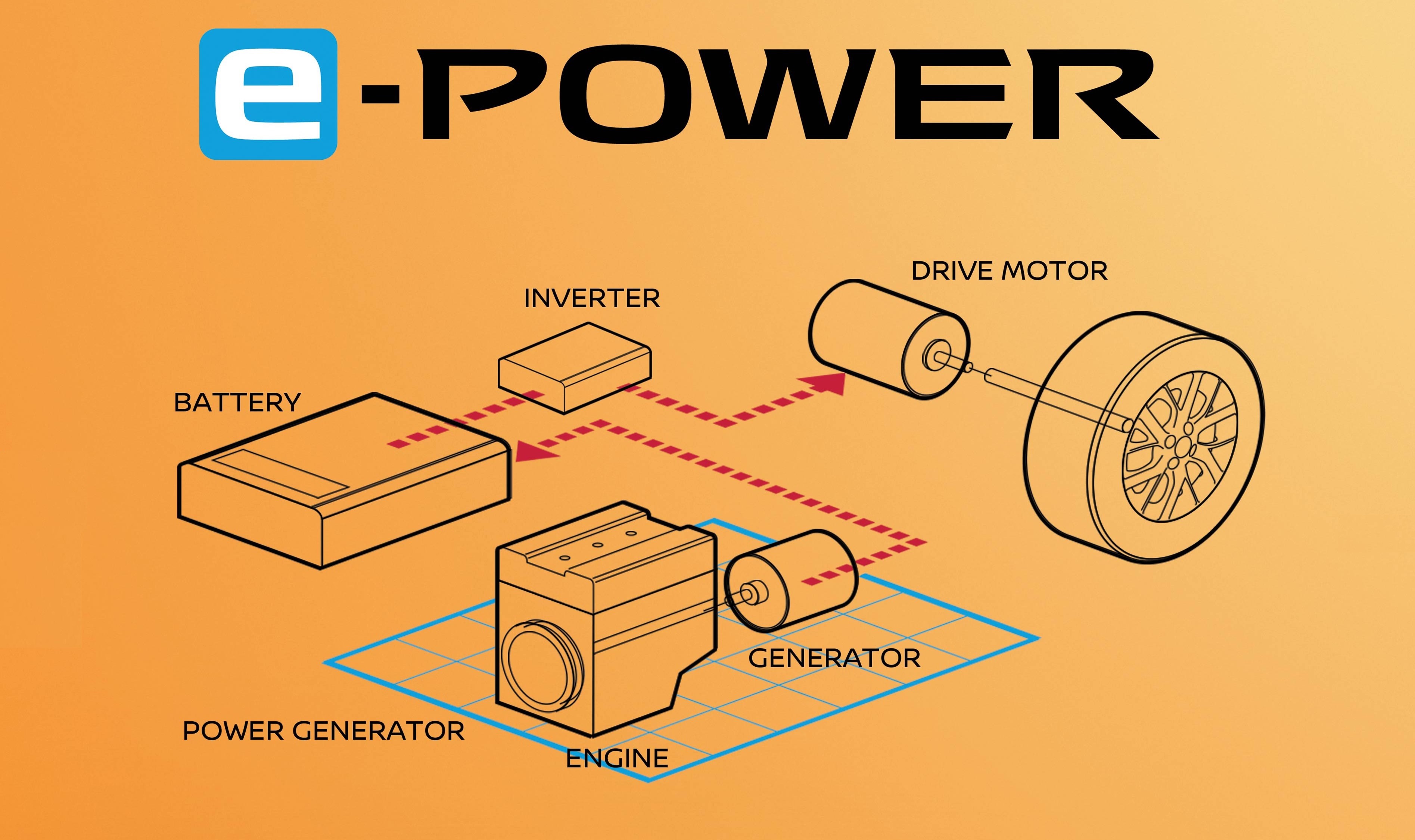
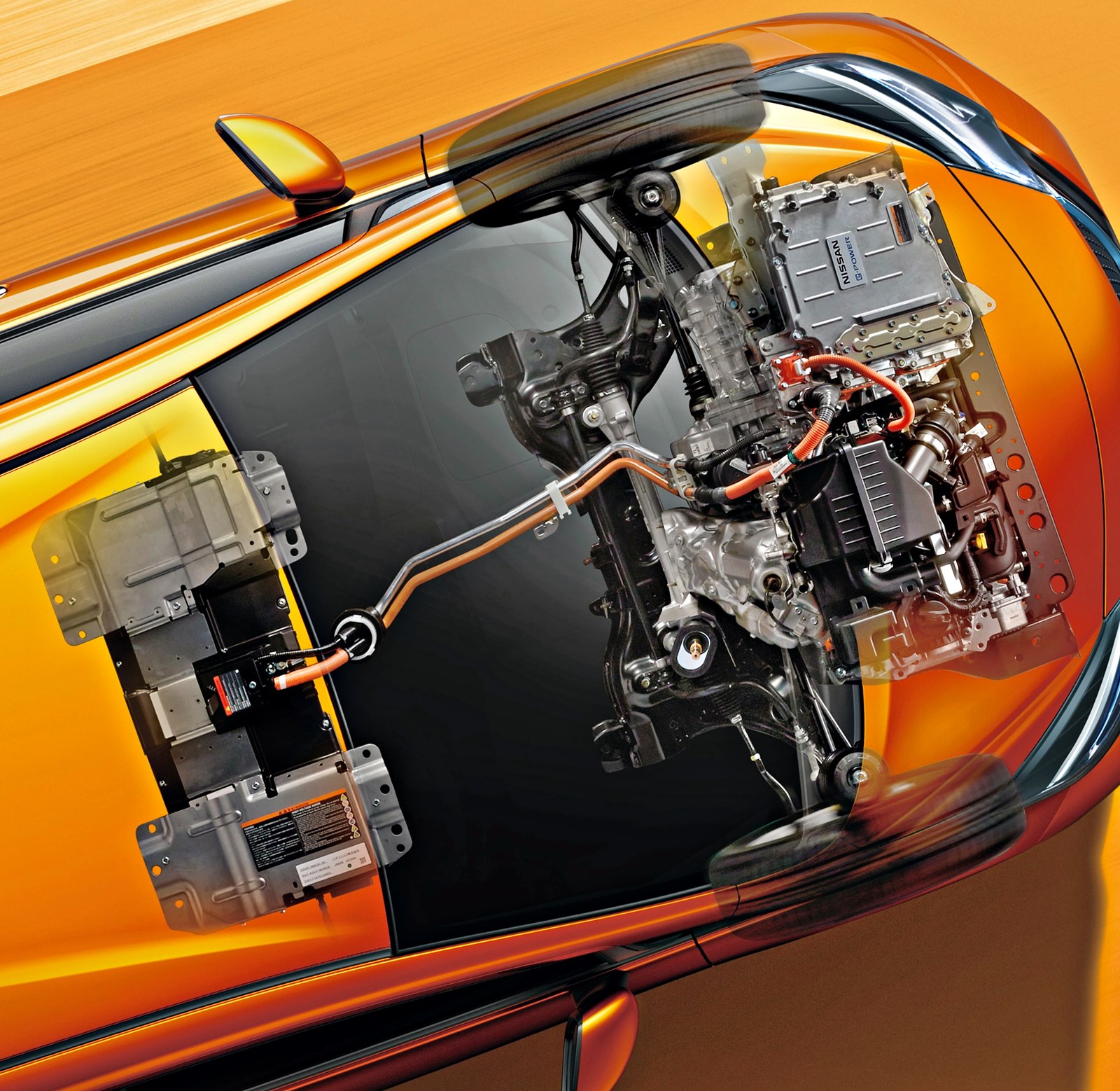
The e-POWER’s compact powertrain consists of a petrol engine, power generator, inverter, and electric motor. In conventional hybrid systems, a low-output electric motor is mated to a petrol engine to drive the wheels when the battery is low (or when traveling at higher speeds). However, in the e-POWER system, the engine is not connected to the wheels; its function is to charge the battery. Thus, the car has its own ‘charging station’ wherever it goes, recharging the battery whenever it is low.
This system structure generally requires a bigger motor and battery because the motor is the only power source to drive wheels. This has made it hard for the automotive industry to mount the system in compact cars. However, Nissan found a way to minimize and reduce weight, develop more responsive motor control methods and optimize energy management. As a result, the e-POWER system can use a smaller battery than the LEAF but delivers EV performance.
This means that there is maximum torque almost instantly – a characteristic of electric motors – , which enhances acceleration. Because the system relies on the engine less frequently, fuel efficiency is comparable to that of leading conventional hybrids, especially during daily town driving.

Over the years, Nissan has been improving and refining the e-POWER system while also offering it in selected models for the Japanese market. It has been progressively offered in other markets since 2020 and this year, the new Qashqai SUV will be the first model in Europe to be equipped with the system. The system was also introduced in China last year in the new Sylphy model.
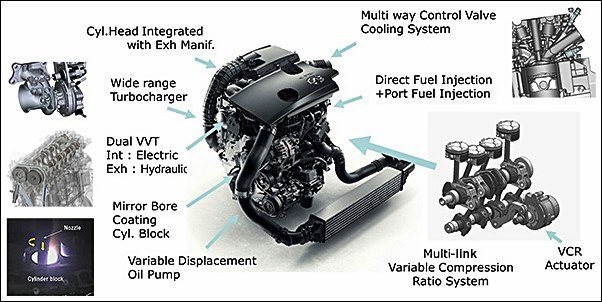
At the heart of the latest e-POWER system is a 1.5-litre 3-cylinder turbocharged variable compression 156 bhp petrol engine (pictured below) which has been developed specifically for this application. First used by Infiniti, the engine’s variable compression capability (between 8.1 and 14.1:1) is a unique feature in an internal combustion engine and allows it to adjust compression ratio, giving both optimum performance and economy depending on the engine load. The 140 kW electric motor is of a similar size and power output as found in Nissan’s EV models.
With the variable compression ratio, the engine runs within its optimal range and best compression ratio, leading to superior fuel efficiency and lower CO2 emissions compared with a traditional internal combustion engine, as well as a refined drive thanks to reduced engine noise.
To maximise performance, in high acceleration or high-speed situations, the energy management control unit within the e-POWER system can send the power generated by the engine directly to the electric motor, via the inverter, to bolster the electricity supply which is coming from the battery. Under deceleration and braking, the kinetic energy is recaptured and channelled back to the battery to optimise efficiency.
Key to the development of the e-POWER system for the Qashqai was the need to ensure the driving experience gave a ‘connected’ sensation, where the petrol engine speed remains relative to the vehicle’s road speed. Engineers at Nissan Technical Centre Europe collaborated in developing a system called ‘Linear Tune’. This feature governs the petrol engine and progressively increases the speed of the 1.5-litre engine to meet the motor’s energy demands as the car accelerates, ensuring there is no ‘disconnect’ between what the occupants experience in terms of performance and sound.

The disparity between engine speed and road speed is a phenomenon that drivers and passengers find unsettling. For example, a sudden rise in engine revs without a commensurate increase in speed is perceived as frustrating and ‘disconnected’ by occupants – which Linear Tune addresses.
Although sales of EVs are growing rapidly, especially in Europe, Nissan understands that not everyone is ready to make the switch for various reasons. The e-POWER system therefore provides a transitional phase where the benefits of using an EV can be experienced without the present concerns that many may have regarding recharging and range.
A chance to become a ‘millionaire’ when purchasing a new Nissan vehicle in March