Sunshine has energy which can be converted into electricity. With that energy source shining down on our planet daily for around 12 hours, it would seem that we should make use of it to power the many different types of modern equipment that we use today. And that is already happening with solar panels collecting sunshine which is converted to electricity for industrial use as well as things like water heaters in homes.
Now that there is this rush towards electrification of cars, why not use solar energy which is unlimited – and costs nothing? Manufacturers are spending billions in developing electric vehicles and surely they would have been able to come out with solar-powered cars by now. After all, they can even use hydrogen in fuel cells to generate electricity which is then used to power cars.
Why are there few solar cars?
The problem is that the technology is still not advanced enough to generate the amounts of electricity constantly to keep a car running. Maybe in the Star Trek age another 250 years in the future, a small solar panel will be enough to power a car indefinitely but at this time, an array of solar panels on a medium-sized car would need around 8 days to fully charge a battery pack of 70 kWh. So it’s a technological issue that is keeping development of solar-powered cars at a snail’s pace for now.
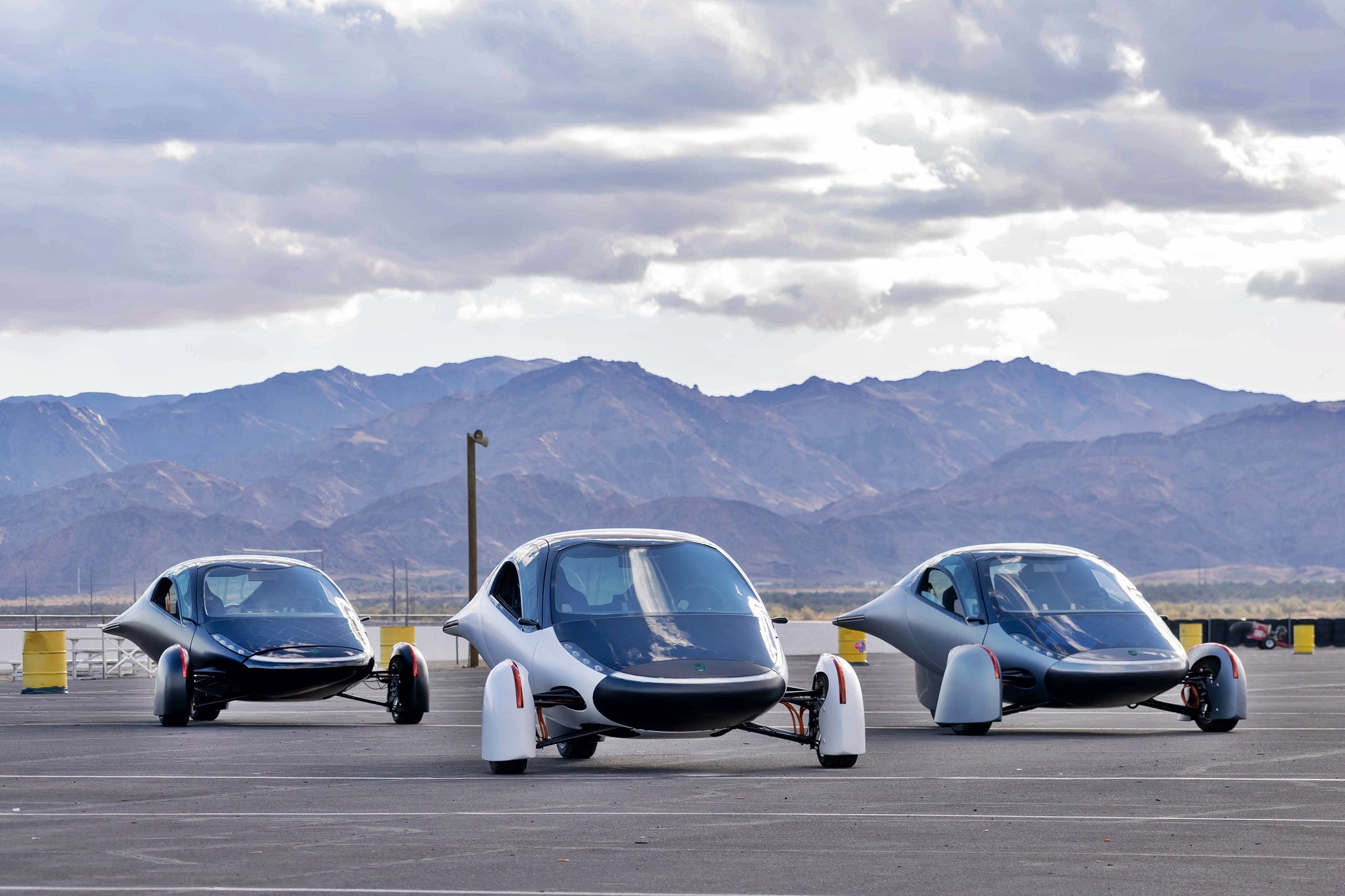
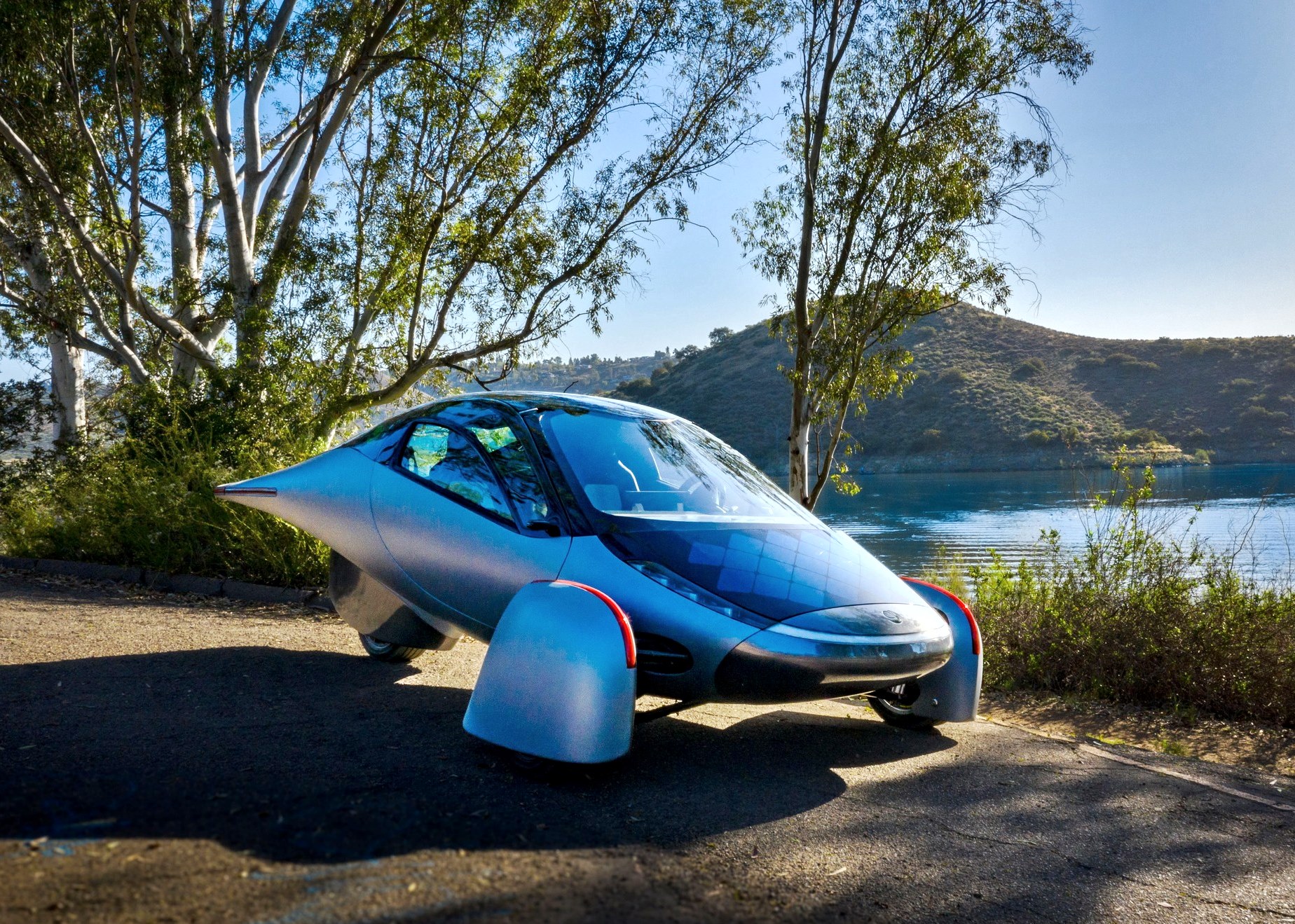
But there are many ongoing efforts and such cars are ‘just around the corner’. In fact, by early 2023, one company might be able to start delivering solar cars to people who have booked one. The company is Aptera, a car company that started in 2005 in California, closed down and was revived in 2019 with a plan to make a battery-electric vehicle (BEV) that also uses solar power primarily, and a battery pack as a range-extender.
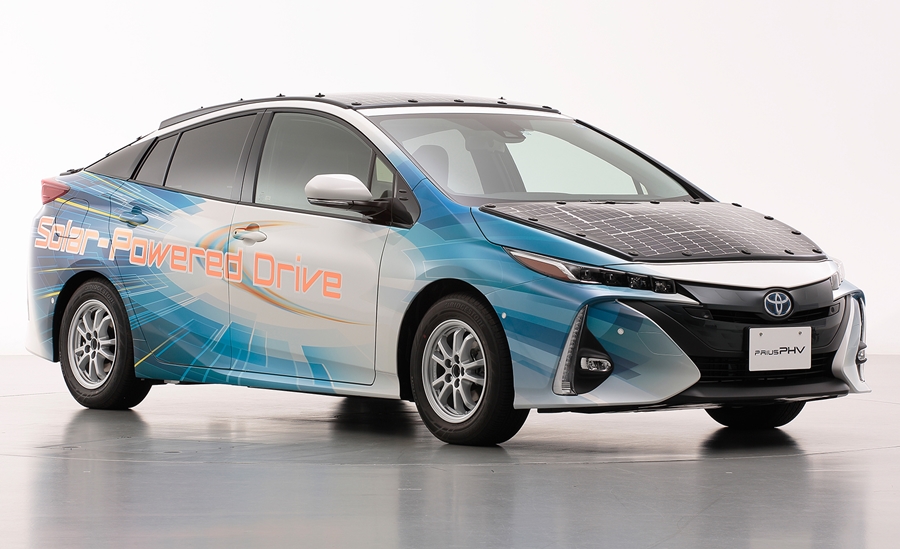
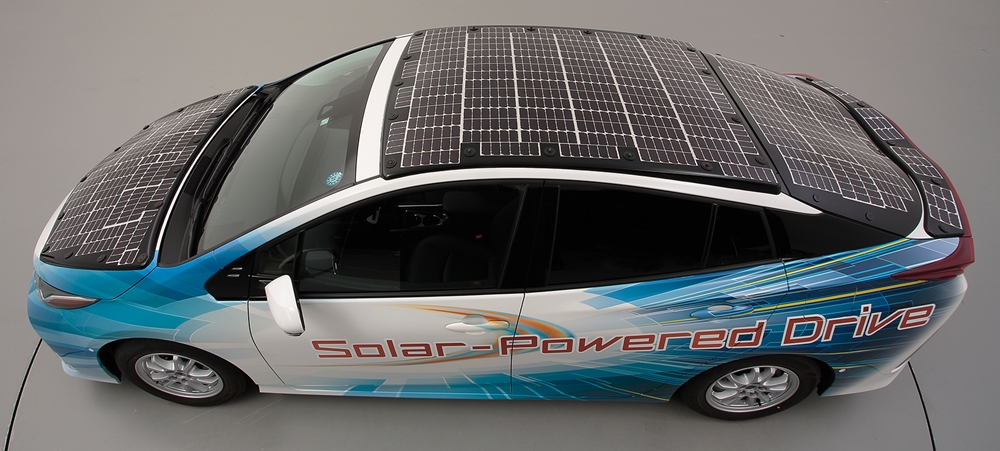
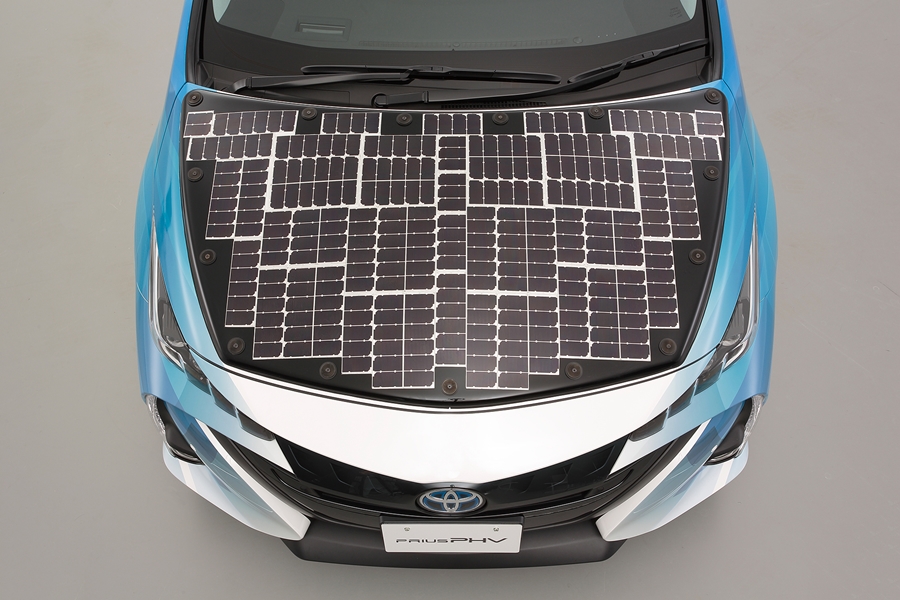
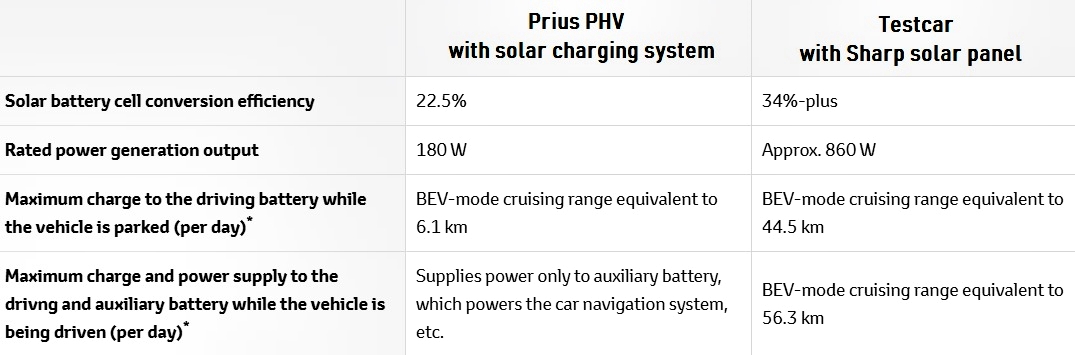
The idea of using solar power as a supplementary energy source for cars is not new. Companies like Toyota and Hyundai have put small solar panels on the roofs of some models for additional electricity to power ancillary equipment.
Up to 1,600 kms range
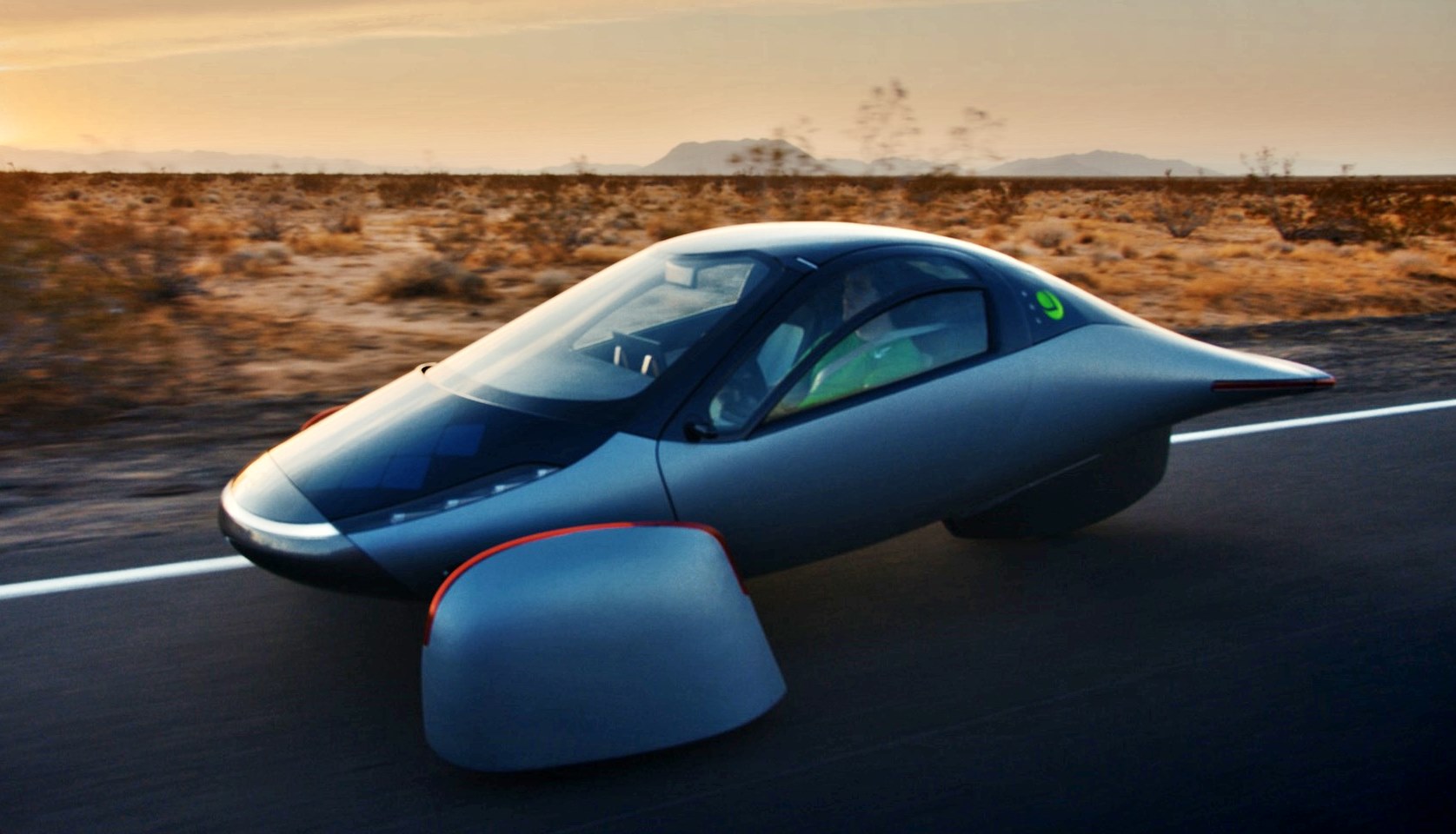
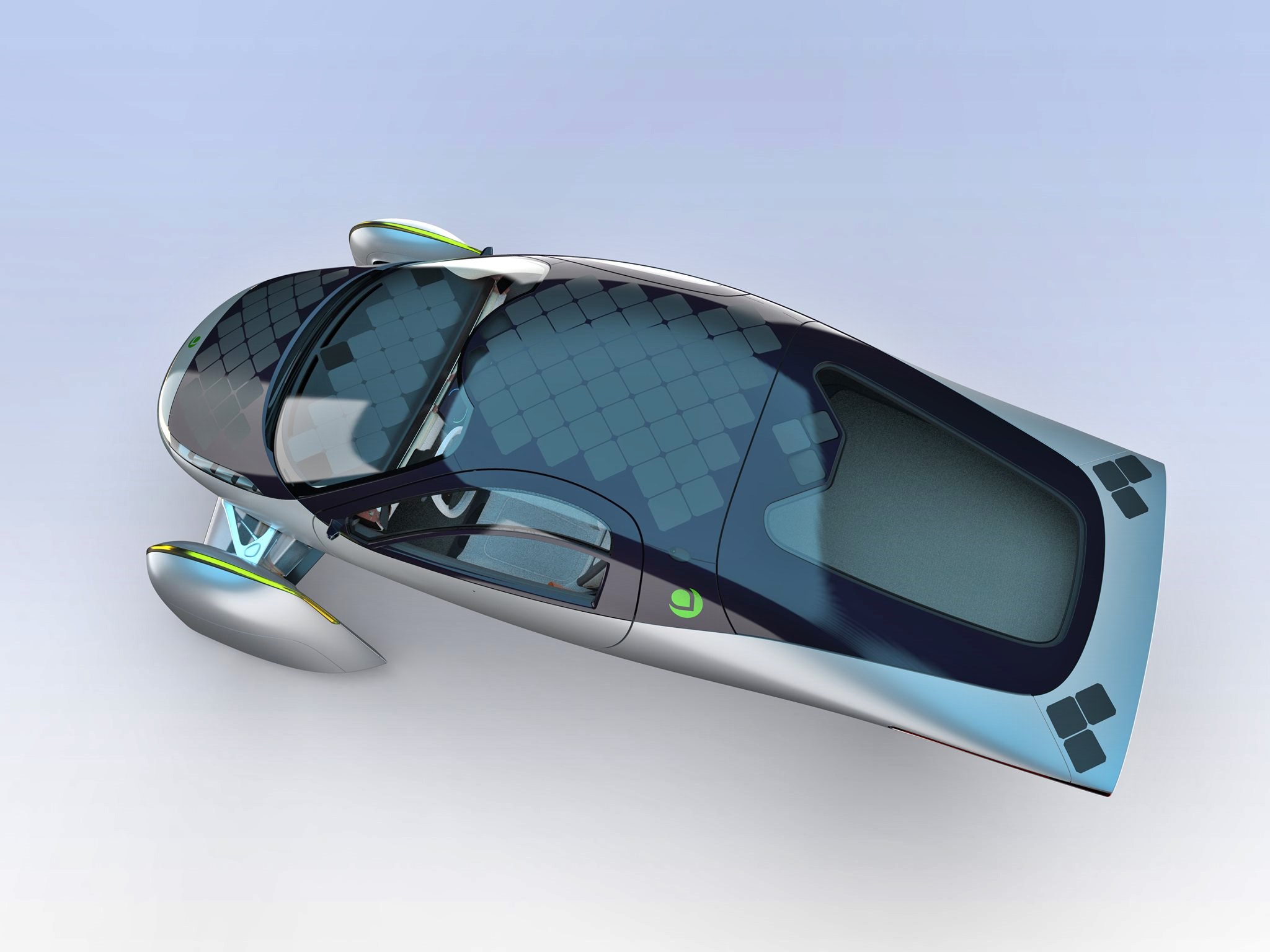
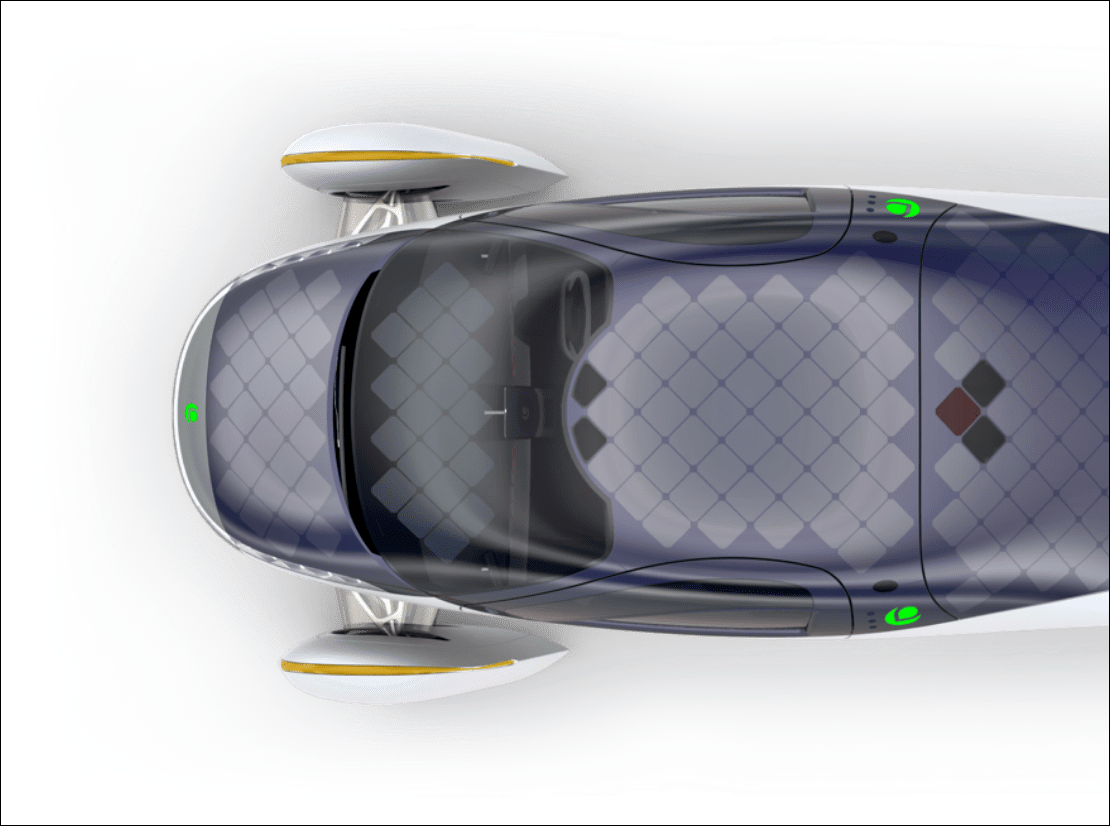
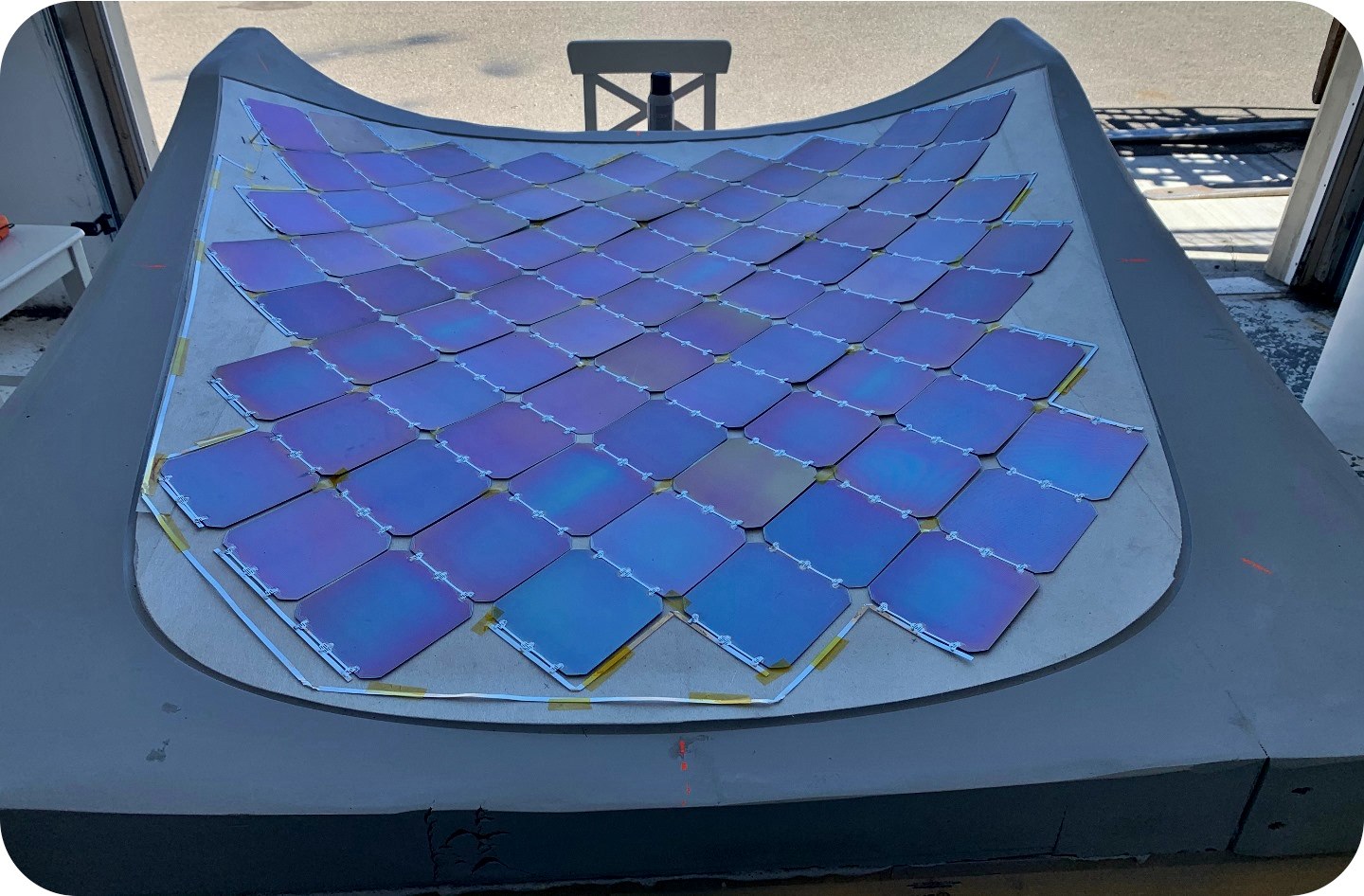
Aptera’s solar electric vehicle (sEV) will require no charging for most daily use and the company claims that it can cover up to 1,600 kms per full charge if the battery pack is used as well. This is achieved with its ‘Never Charge system which uses 180 cells on diamond-shaped solar panels covering 3 square metres of the car’s body. These can collect sunshine to convert to as much as 700W which would be good for 64 kms of driving per day. Those 64 kms of essentially free range are collected by over 3 square metres of solar panels on the bodywork.

If you’re just driving around town daily, then you really would not need to recharge. But for longer distances, then there is a battery pack which has stored electricity to provide the extra range required. And Aptera says that recharging can be done with a household power supply, though how long it will take is not mentioned.
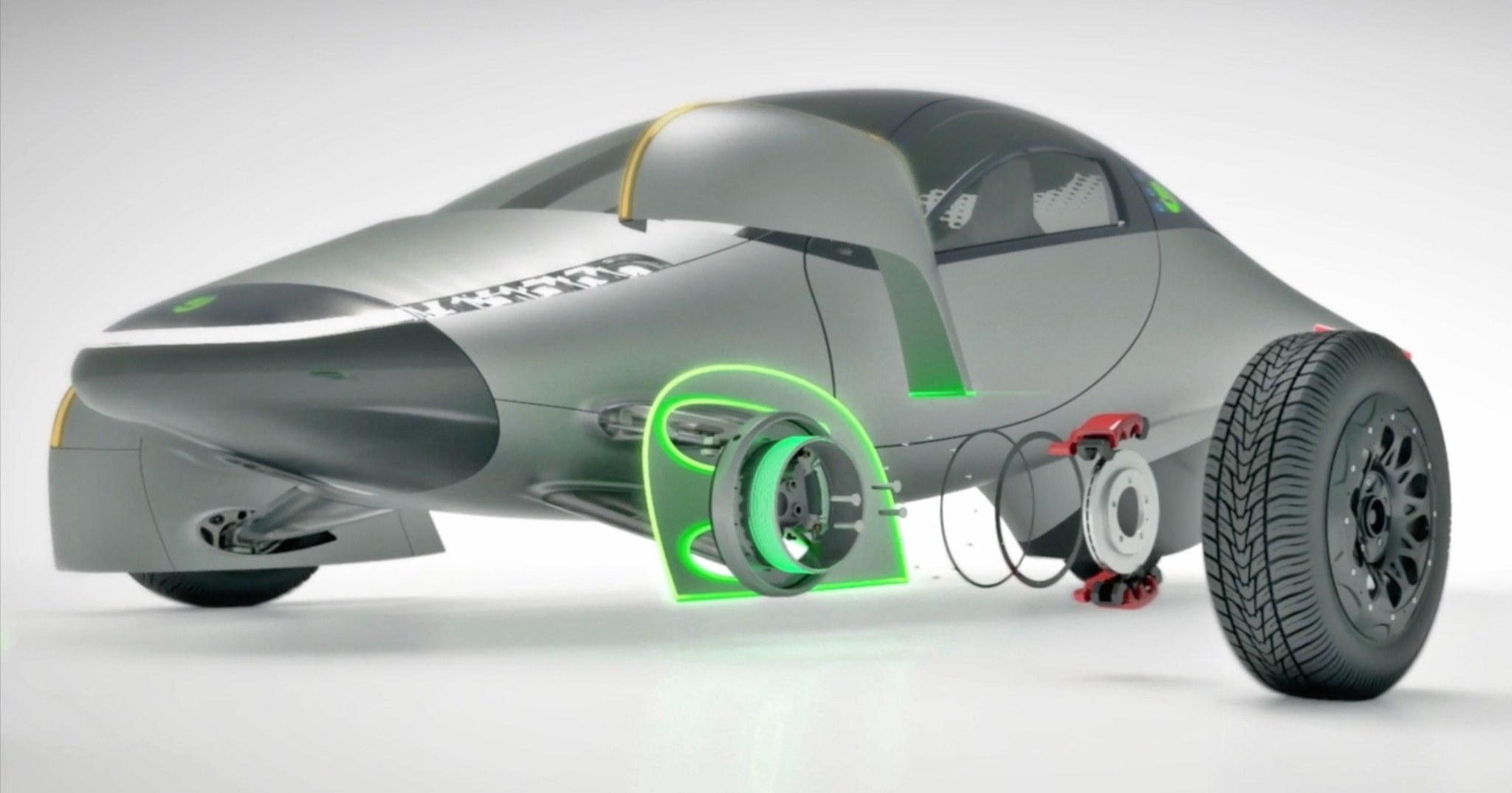
Propulsion is by 3 liquid-cooled in-wheel electric motors (two in front, one behind) that can give an acceleration time of 3.5 seconds from 0 to 96 km/h and a top speed claimed to be almost 180 km/h. For stability, there will be all-wheel drive and vectorized torque control.
Three wheels, instead of four
To maximize use of the electricity available, the sEV has to be as light as possible, requiring less energy to move. In fact, having three wheels instead of four is partly due to saving weight. At between 818 kgs to 1,000 kgs, the vehicle is said to weigh 65% less than other EVs on the market today. Aptera’s engineers have also used many different example to reduce energy loss, and by eliminating the fourth wheel, the contact point for friction and potential energy loss is lessened.
The body is built with ultra-lightweight composites and its arched shape mimics the physics of an eggshell to create a safety cell that is claimed to be much stronger than steel.
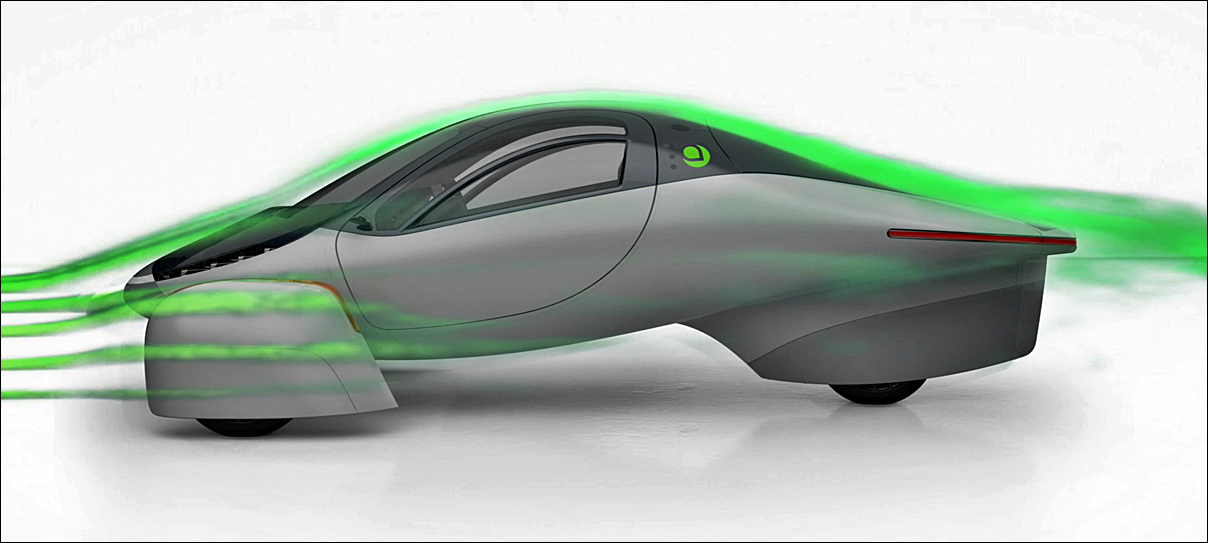
Aerodynamic efficiency of 0.13 Cd
Besides light weight, the other important factor is aerodynamic efficiency or how slippery the shape can be so that wind resistance is minimized. Less energy will be needed to overcome the wind resistance so performance will be better and at the same time, the energy saved can be used for extending range.
The aerodynamic form of the vehicle, which has a Cd of 0.13, is inspired by nature. The teardrop-shaped central body allows air to flow around it to ‘follow & copy’ that shape. This means airflow contacts the body at a certain angle around the front wheel area, as the air is being bent around the tapered nose. The wheel covers are tapered inward and the rear is tapered outward, making the overall shape more aligned with the main bodywork.
At the single rear wheel, the story is different. The wheel is positioned at the centreline of the vehicle and optimizations were applied to the bodywork in front of the wheel. Guiding the air in such a way that it avoids hitting the exposed part of the tyre, providing gains in terms of aerodynamic efficiency.
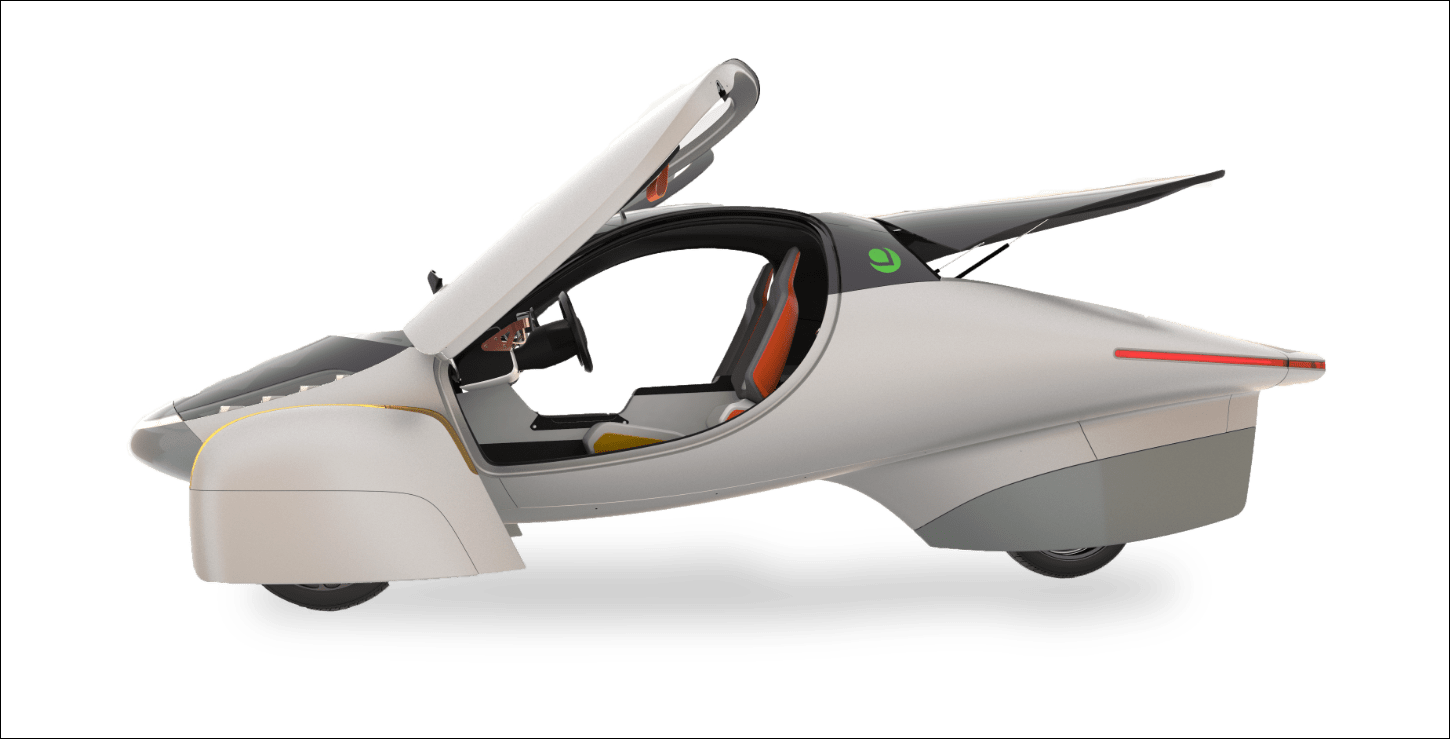
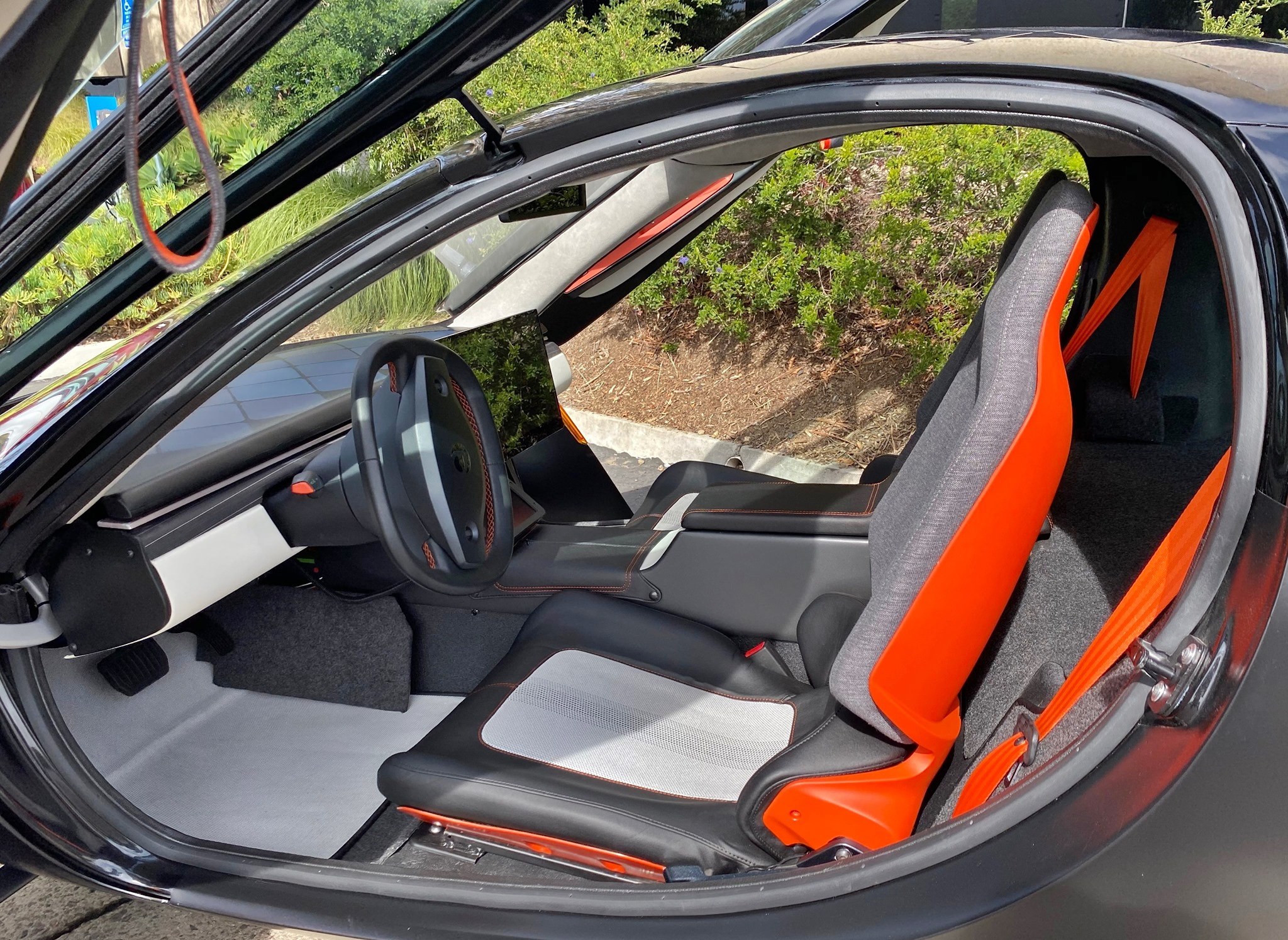
Intelligent cabin packaging
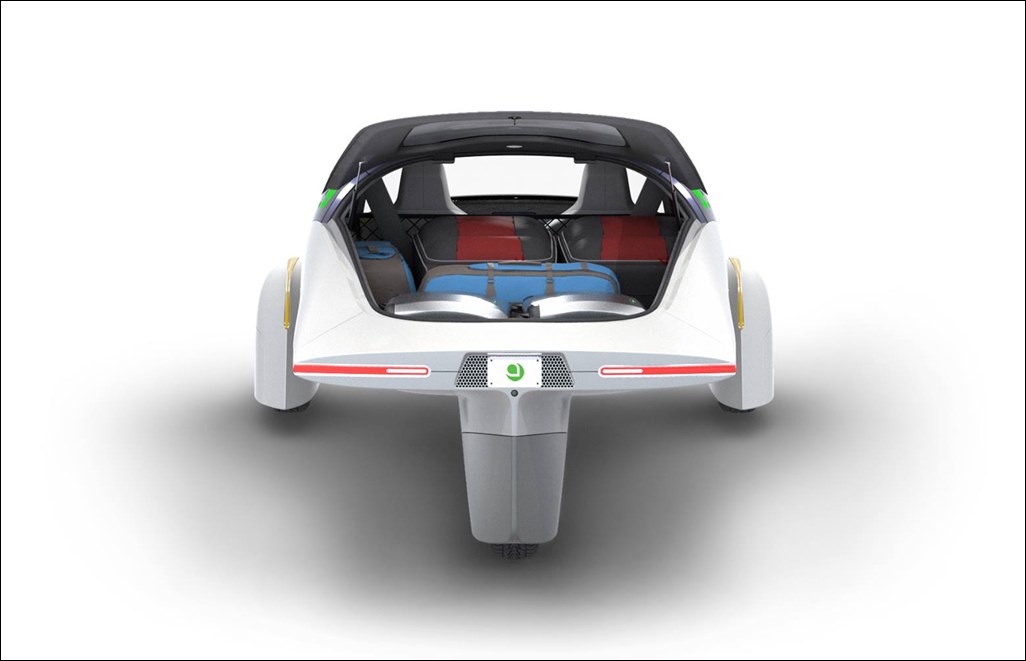
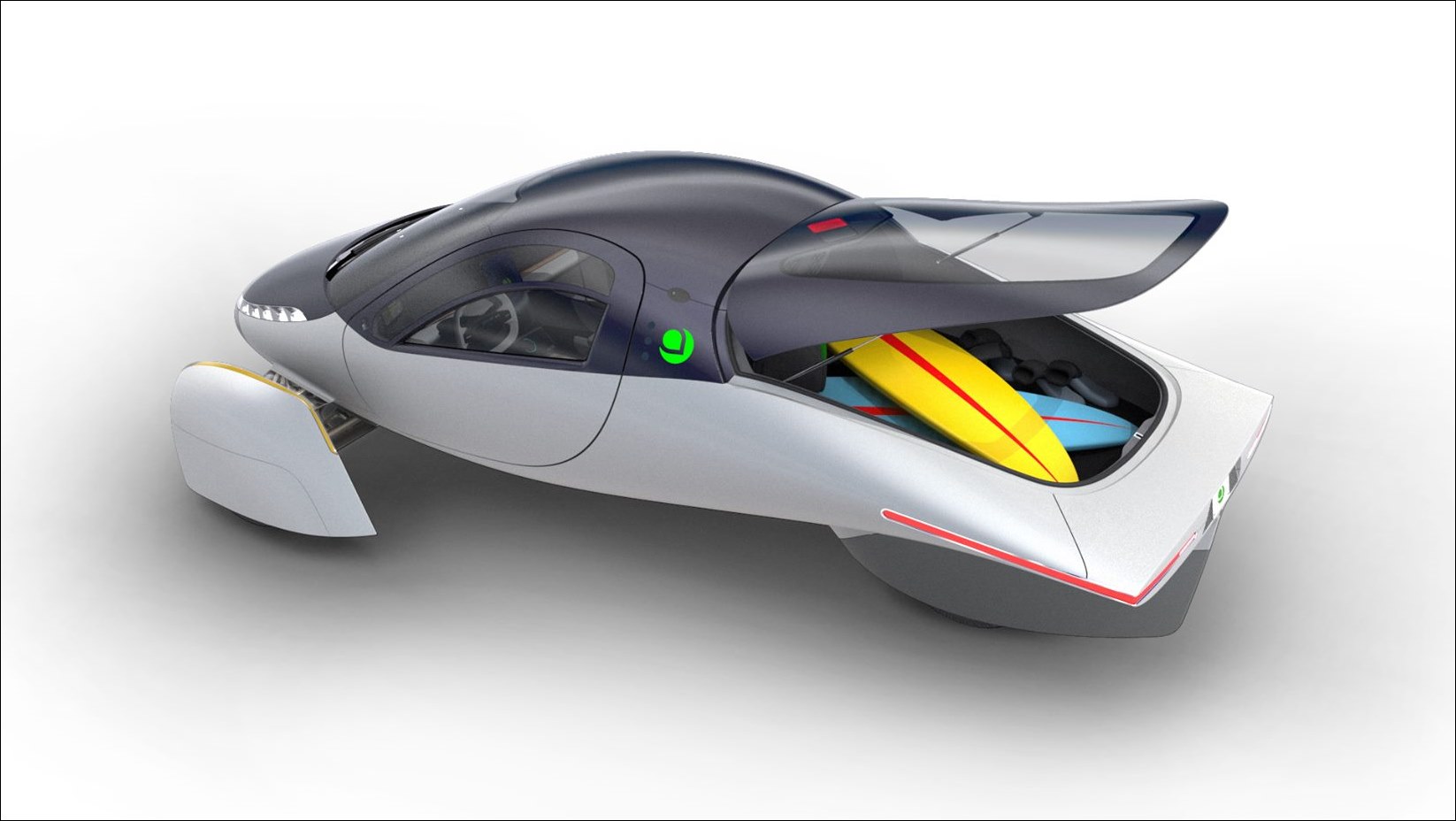
The sEV is a small vehicle and seats only two. However, intelligent packaging has ensured that those two people can carry a lot of gear or a lot of shopping from the supermarket. The layout has both occupants side by side, rather than in a tandem position like a motorcycle (as some solar vehicles have been designed). Much of the thinking behind the interior has been with manufacturing simplicity and flexibility in mind.
As would be expected, there are storage areas for the stuff we all carry these days as well as things like wireless charging pads. Environmentally-conscious materials are used, such as biodegradable and plant-based leather, recycled PET and 3D knit materials, bio-based plastic thread and recycled felt.
Pricing to be from US$29,500
Aptera is confident of moving into the production phase by the end of this year as it has received US$40 million (about RM178.3 million) in crowdfunding and commitments. It has also been accepting $100 (RM446) deposits from interested customers (it says there are already 25,000 reservations) and expects to price their first solar vehicle from US$29,500 (about RM131,500).
Free sunshine helps Proton save up to RM5.85 million on electricity costs