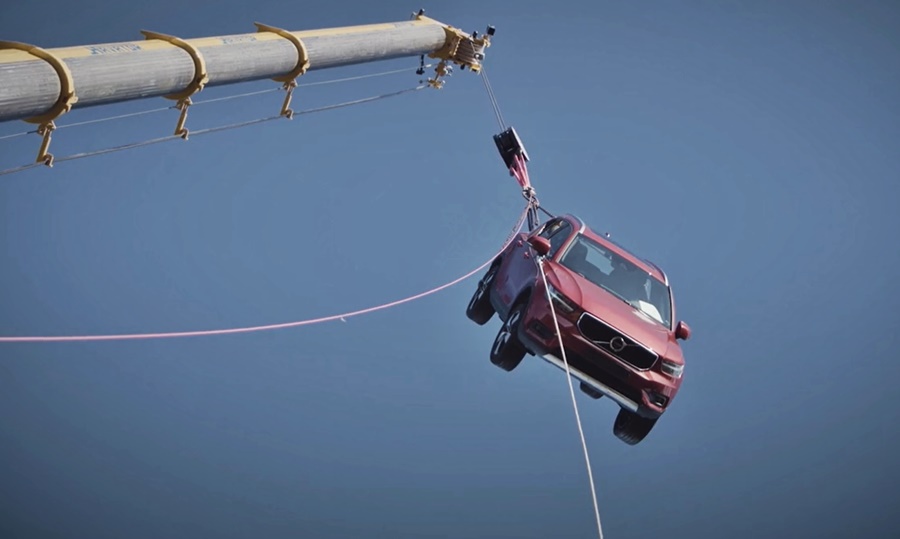
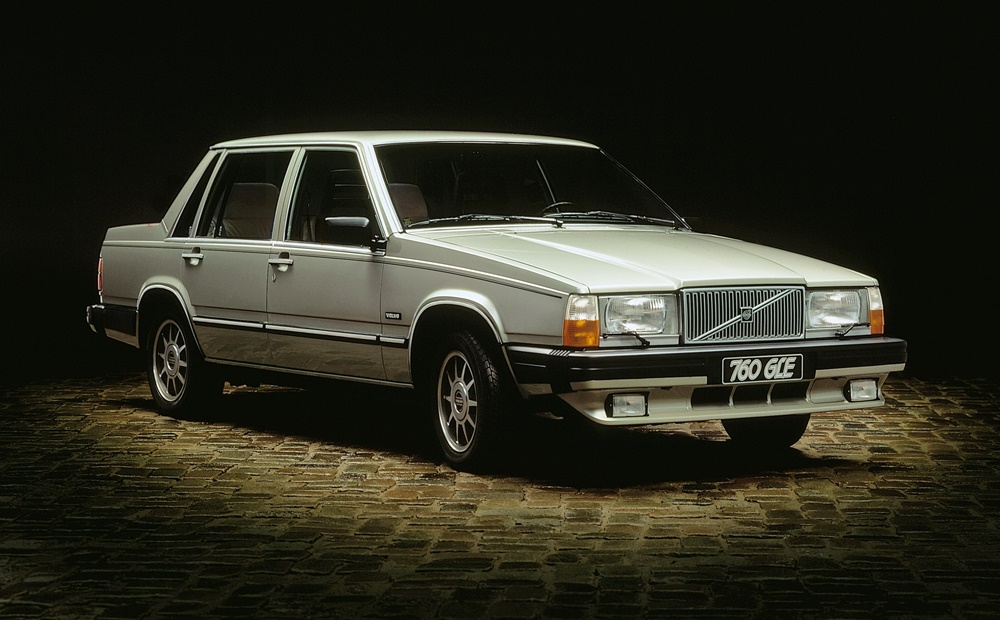
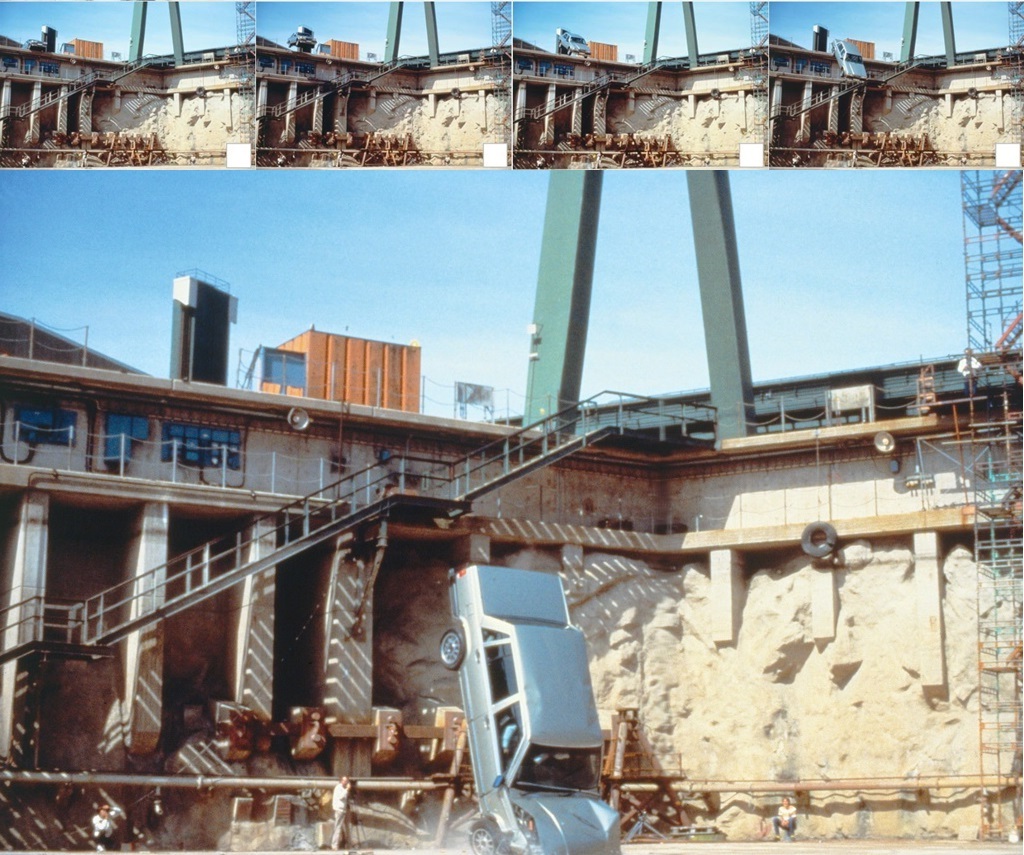
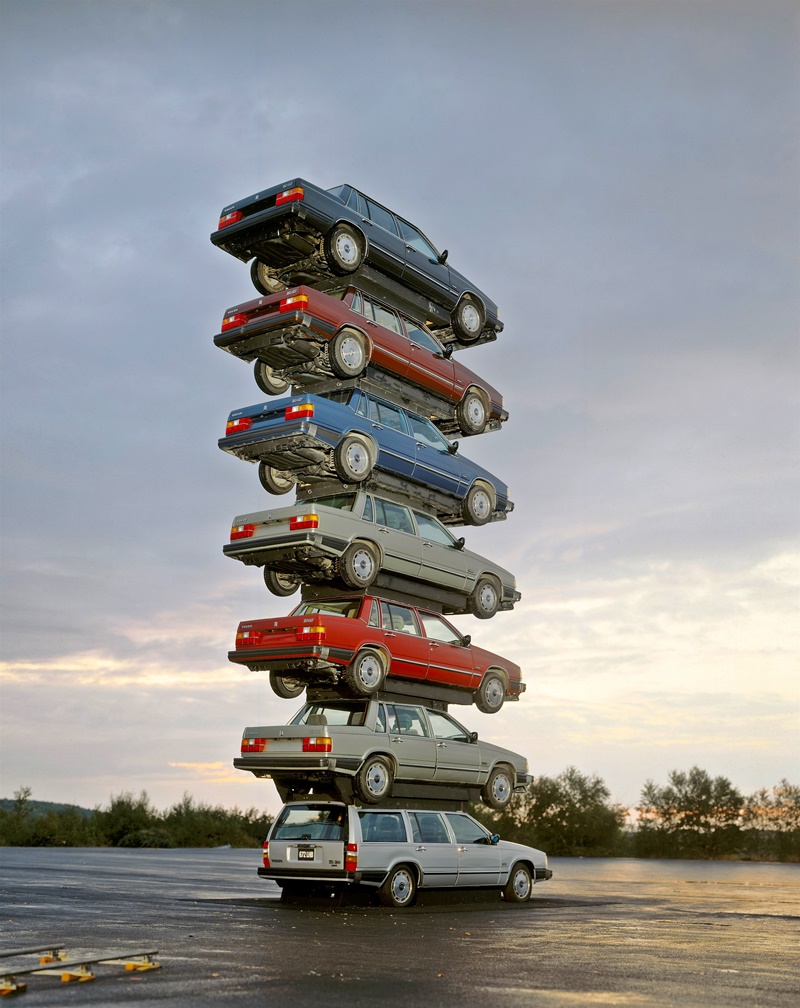
Volvo Cars recently conducted its most extreme crash test ever, and it was not within the advanced Safety Centre but outdoors – with cars dropped from a crane! Ten Volvos, of different models, were dropped several times from a height of 30 metres.
Before the drop, Volvo Cars safety engineers made exact calculations about how much pressure and force each car needed to be exposed to, in order to reach the desired level of damage.
Simulating extreme accidents
The purpose: to help rescue services to prepare for any possible crash scenario and to simulate the forces that erupt in the most extreme crashes, beyond what can be simulated with ordinary crash testing.
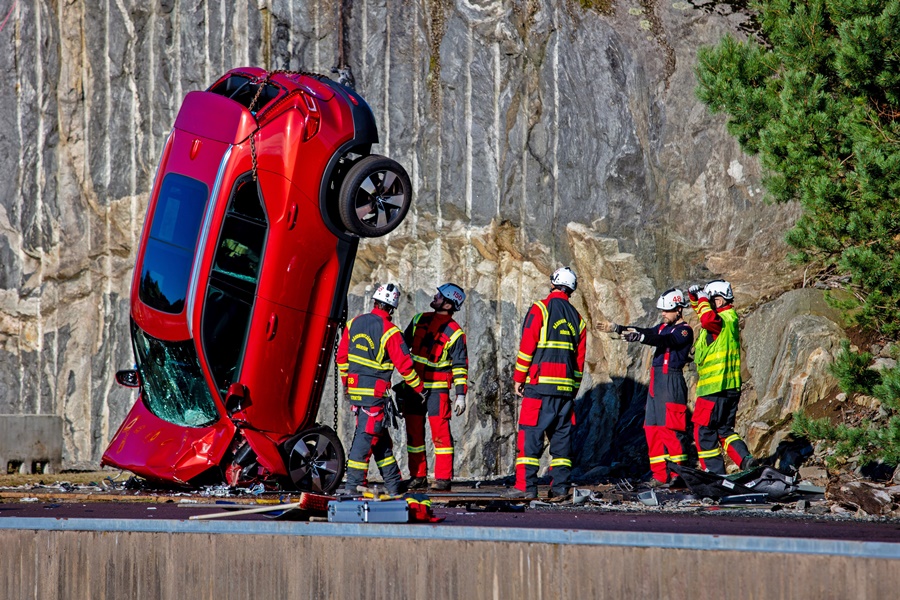
This unusual approach helped create enough damage to adequately simulate the damage found in the most extreme crash scenarios. All findings from the crashes and the resulting extrication work will be collected in an extensive research report. This report will be made available free of use to rescue workers elsewhere, allowing them to benefit from the findings and further develop their life-saving procedures and capabilities
Similar extreme test in 1985
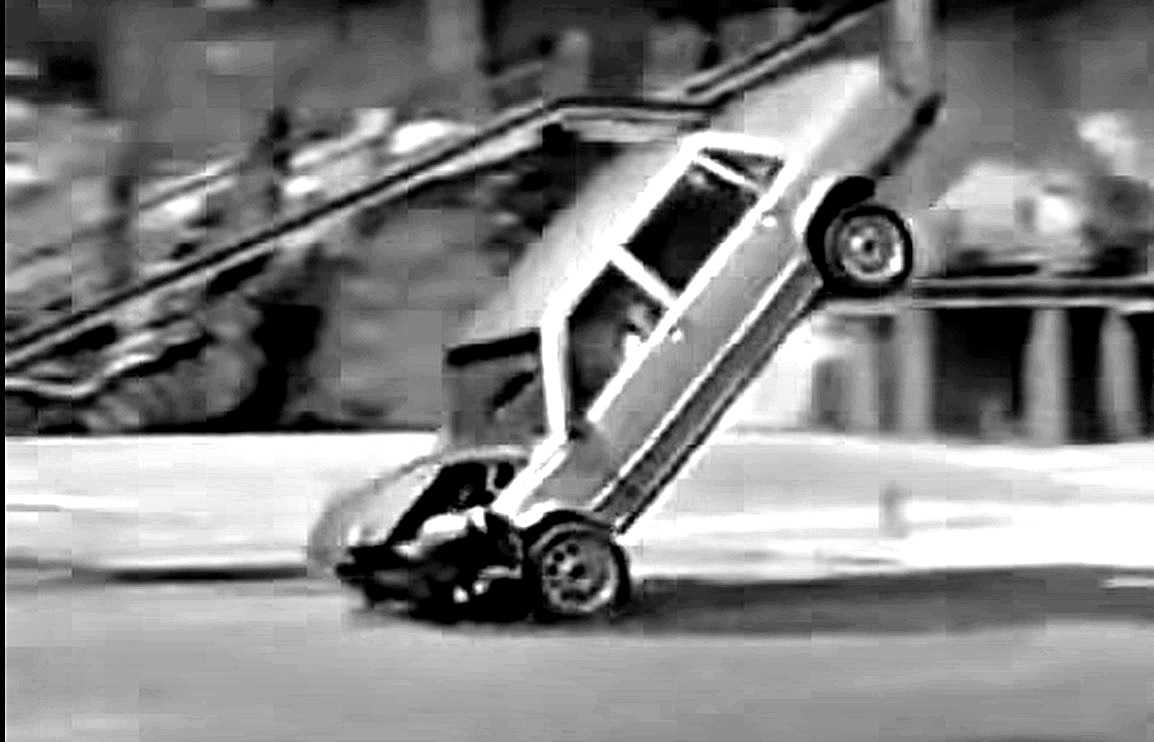
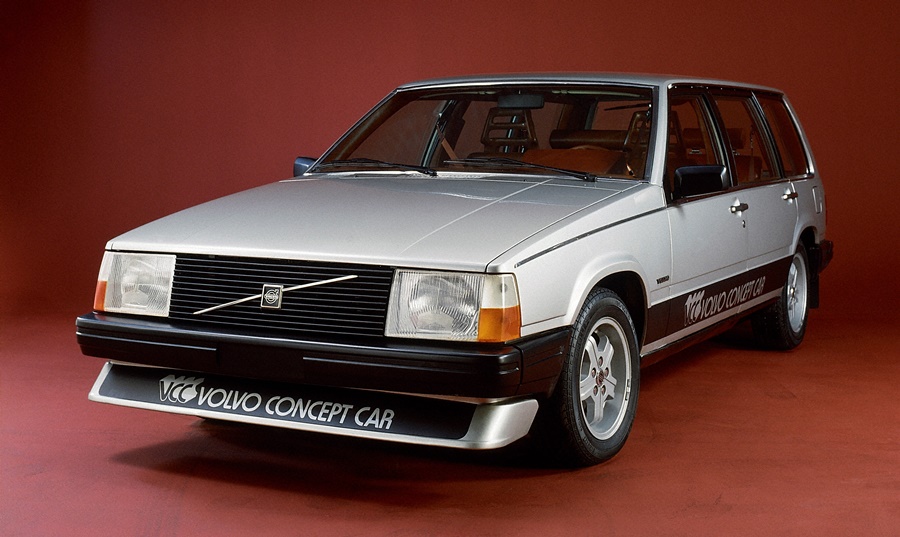
The crash test conducted recently was not really Volvo’s first extreme test: 35 years ago, its American subsidiary had a then-new 760 driven off a building and it fell 14 metres, hitting the ground nose-first. The impact was equivalent to a frontal collision at 50 km/h, the front end crumpling as it was ‘programmed’ to do so in order that the impact energy could be absorbed.
Back then, there was no GoPro and no drones for recording and conventional video equipment was used. Nevertheless, the resulting video – which was like a scene from an action movie – provided scary views from the seats through the windscreen as the ground rushed up.
At that time, the ‘crash’ was done not for helping rescue workers understand what a severely crashed car is like but more for promoting the safety of Volvos, and particularly the crucial value of using seatbelts.
Today’s cars are stronger
In the 1980s, the construction of most cars was fairly conventional with basically steel and plastic materials that could easily be cut. They were as safe as could be during that era, with Volvos being among the best in occupant protection. However, many of today’s cars use stronger materials, with the latest Volvos made of some of the hardest steel found in modern cars. They have more complex structural designs, and the presence of high-voltage electrical systems and battery packs in hybrid models must also be considered.
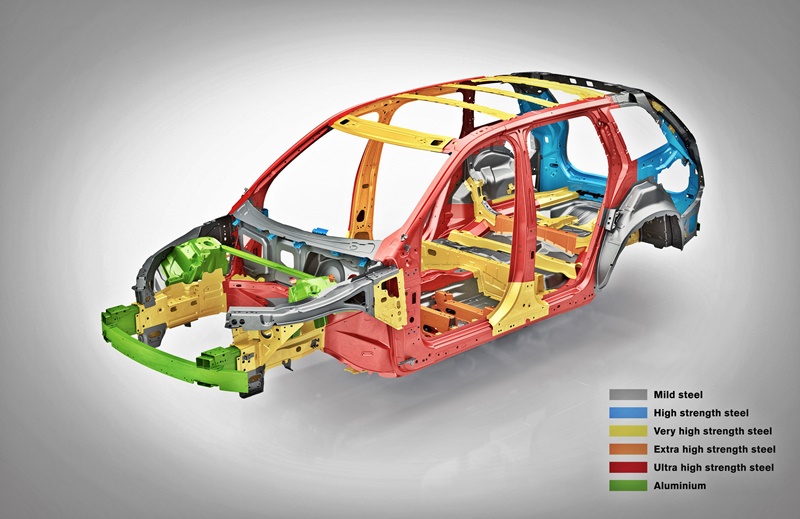
Volvo therefore continuously crashes its cars, the recent one being an example, in order to get information on how the structure deforms. This will help rescuers who may use hydraulic rescue tools known in the industry as ‘jaws of life’. Extrication specialists often talk about the golden hour: the time-span they need to get injured occupants out and to the hospital for treatment.
Usually, rescue workers get their training vehicles from scrapyards. But these cars are often up to two decades old. And in terms of steel strength, safety cage construction and overall durability, there is a vast difference between modern cars and those built 15 to 20 years ago – like the 760 in the video.
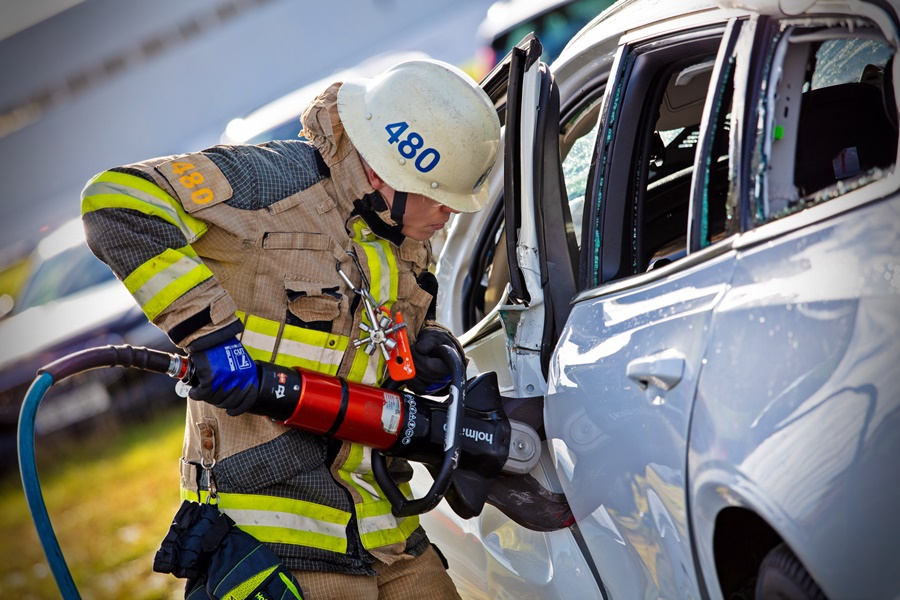

This makes it crucial for rescue workers to constantly update their familiarity with newer car models and review their processes, in order to develop new extrication techniques. In other words, these training sessions can mean the difference between life and death. So at the request of the rescue services, Volvo Cars decided to step things up a notch.
“Normally we only crash cars in the laboratory, but this was the first time we dropped them from a crane,” said Hakan Gustafson, a senior investigator with the Volvo Cars Traffic Accident Research Team. “We knew we would see extreme deformations after the test, and we did this to give the rescue team a real challenge to work with.”