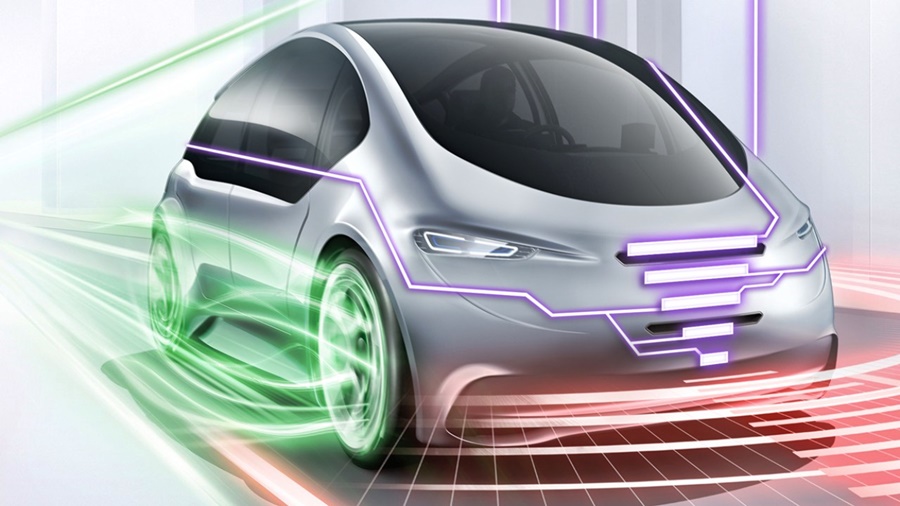
Human beings have two eyes to view their surroundings as they drive, sending images to the brain which then makes the necessary decisions to brake or avoid hazards. When an on-board computer takes over the entire job of operating an autonomous car, two ‘eyes’ are not enough and a third sensor is needed. The first two eyes – already in use – are the camera and radar and the third is a long-range lidar sensor for light detection and ranging.
Bosch has a production-ready lidar system that is suitable for automotive use. This laser-based distance measurement technology is indispensable for driving functions at SAE Levels 3 to 5 (the different levels of autonomy). The new sensor will cover both long and close ranges – on highways and in the city.
By exploiting economies of scale, Bosch aims to reduce the price for the sophisticated technology and make it affordable for the mass market. “By filling the sensor gap, Bosch is making automated driving a viable possibility in the first place,” said Bosch Management Board Member, Harald Kroeger.
Alert to all automated driving situations
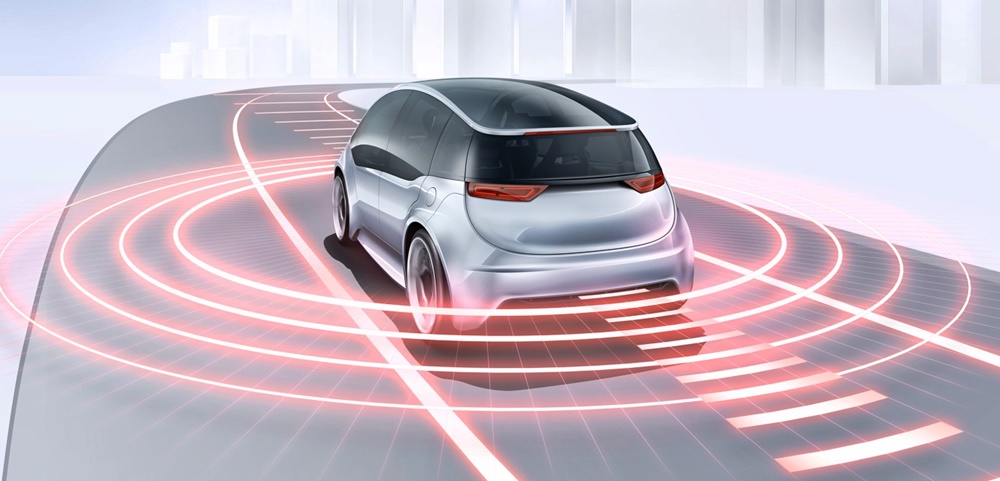
Only the parallel deployment of three sensor principles ensures that automated driving will offer maximum safety when it is available. This has been confirmed by Bosch analyses, where developers investigated all use cases of automated driving functions – from highway assist to fully automated driving in cities.
For example, if a motorcycle approaches an automated vehicle at high speed at a junction, lidar is needed in addition to camera and radar to ensure the reliable sensing of the two-wheeler. In this instance, radar can struggle to detect the bike’s narrow silhouette and plastic fairings. Moreover, a camera can always be dazzled by harsh light falling on it. As such, there is a need for radar, camera, and lidar, with the three technologies complementing each other perfectly and delivering reliable information in every driving situation.
Lidar is an essential element
We can think of laser as a ‘third eye’: in lidar systems, the sensor emits laser pulses and captures the laser light that is scattered back. The system then calculates distances based on the measured time it takes for the light to bounce back. Lidar offers very high resolution with a long range and a wide field of vision. As a result, the laser-based distance measurement tool can reliably detect even non-metallic objects at a great distance, such as rocks on the road. This means there is plenty of time to initiate driving manoeuvres such as braking or swerving.
At the same time, using lidar in vehicles exposes the lidar system’s components, such as the detector and the laser, to many stresses – above all, with regard to temperature resistance and reliability over the vehicle’s entire lifetime. Because Bosch can draw on its sensor expertise and systems know-how in the fields of radar and camera technology when developing the lidar, the company can ensure that all three sensor technologies dovetail with each other.
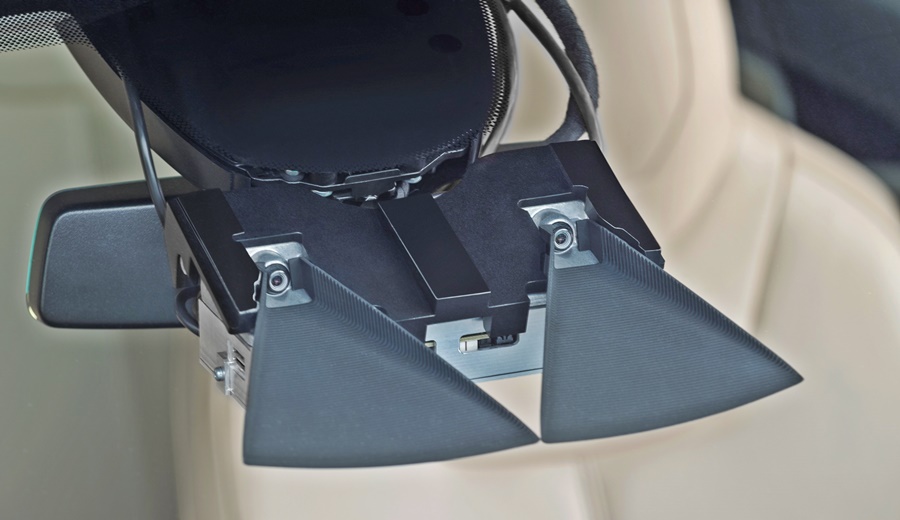

“We want to make automated driving safe, convenient, and fascinating. In this way, we will be making a decisive contribution to the mobility of the future,” said Kroeger. Bosch’s long-range lidar will fulfil all safety requirements for automated driving as well as enable automakers to efficiently integrate the technology into a very wide range of vehicle types in the future.
Artificial intelligence makes systems even safer
Recently, Bosch engineers succeeded in taking the camera technology used in cars to a new level by enhancing it with artificial intelligence. The camera technology detects objects, categorizes them into classes such as vehicles, pedestrians, or bicycles, and measures their movement. In congested urban traffic, the camera can also recognize and classify partially obscured or crossing vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists quickly and reliably. This allows the vehicle to trigger a warning or an emergency braking manoeuvre as required.
The engineers are also continuously refining radar technology. The latest generation of Bosch radar sensors is even better at capturing the vehicle’s surroundings – even in bad weather or poor light conditions. Their greater detection range, wide aperture, and high angular separability are the basis for this improved performance.